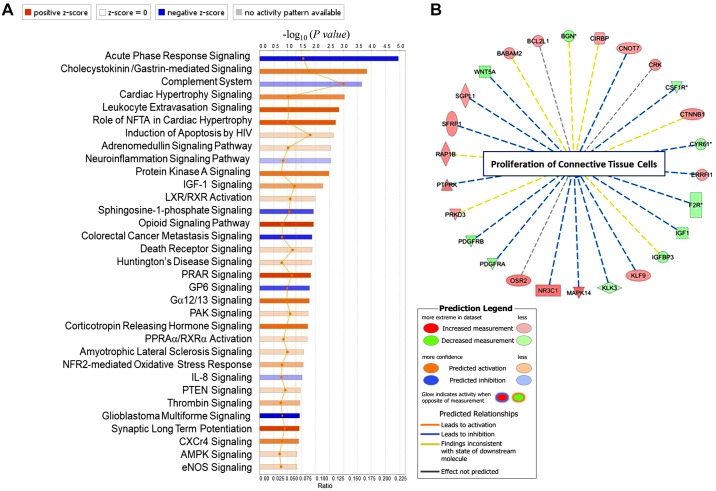
Fig. 6.
Differential gene expression pattern between wild-type (WT) and C1r−/− mouse kidney tissue. A: differentially expressed genes (fold change ≥ 1.5, P ≤ 0.05) analyzed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software showng canonical pathways with positive and negative z scores. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway was significantly upregulated and complement system significantly downregulated in C1r−/− mice compared with WT mice. The canonical pathways tab displays the most significant canonical pathways across the entire data set. The significance values for the canonical pathways were calculated by Fisher's exact test (right-tailed). The significance indicates the probability of association of molecules from the current data set with the canonical pathway by random chance alone. The orange- and blue-colored bars indicate predicted pathway activation or predicted inhibition, respectively (z score). The intensity of the colors (from light to dark orange and blue) indicates values of the z score for each bar associated with a unique pathway (from lower to higher). The significant canonical pathways for the data set that are involved in the analysis are displayed along the x-axis. The y-axis displays the −log of the P value that was calculated by a Fisher's exact test (right-tailed) such that taller bars equate to increased significance. The orange points connected by a thin orange line represent the ratio. The ratio was calculated as follows: number of genes in a given pathway that meet your cutoff criteria ÷ the total number of genes that make up that pathway and that are in the reference gene set. B: analysis of disease functions showing inhibition of proliferation of connective tissue cells and the genes downregulated or upregulated in C1r−/− mice compared with WT mice. NFTA, nuclear factor of activated T cells; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IGF-I, insulin-like growth factor-I; LXR/RXR, liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor; GP6, glycoprotein VI; PAK, p21-activated kinases; PPRAα/RXRα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor/retinoid X receptor; NFR2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; IL-8, interleukin-8; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; CXCr4, chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase.