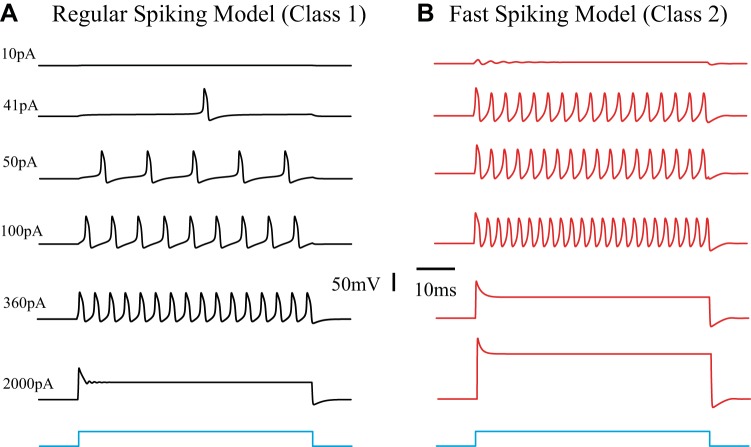
Fig. 5.
Response characteristics of the regular-spiking (RS) and fast spiking (FS) models. Neuronal response profiles are frequently grouped into 3 classes, as first defined by Hodgkin (1948). The underlying nonlinear dynamics and bifurcations can be described by using different parameter sets in Eq. 1. The parameters used for this figure are summarized in Table 1. A: an excitatory pyramidal cell model of the RS type with Class I properties. B: an inhibitory cell model of the FS type with class II excitability. In addition, it can be seen that saturation at high input levels occurs at a much lower level for the inhibitory cells than for the larger pyramidal neurons (360 pA vs. 2,000 pA).