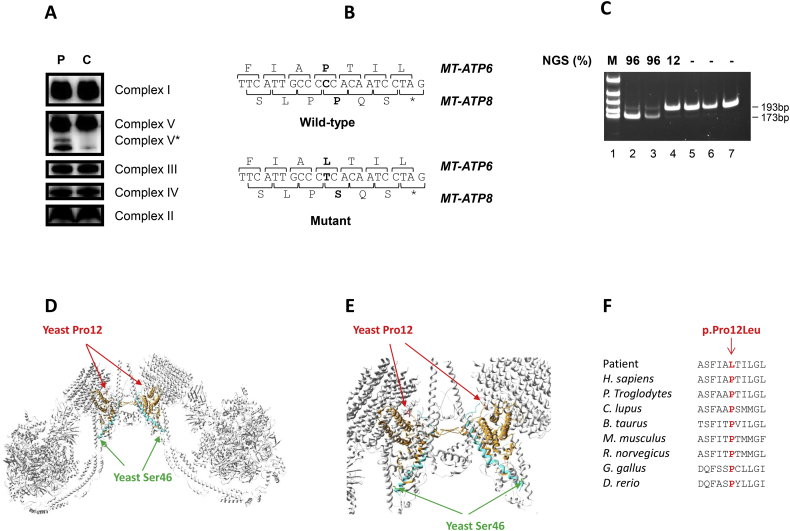
Fig. 1.
A novel m.8561C>T variant associated with early-onset neurological phenotype. A. BN-PAGE in muscles of control subject (C) and patient (P). The amount of subcomplex F1 is increased in the patient and V* corresponds to the supplementary band detected by the anti-complex V antibody. (C) is matched for age and gender to the patient. B: WT and mutated mtDNA sequences obtained by NGS. C: PCR-RFLP analysis of m.8561C>T in different tissues from the patient (lane 2: muscle, lane 3 blood), his mother (lane 4: urinary epithelial cells, lane 5: buccal swab, lane 6: blood) and a negative control (lane 7). M: molecular weight marker. Mutant loads detected by NGS are indicated (top): 96% in patient's muscle and blood, 12% in patient's asymptomatic mother urines and approximatelly the same load in her blood and buccal swab. D–E: Localization of the concerned amino acids on the crystallographic structure of S. cerevisiae mitochondrial ATP synthase (e: higher magnification). The MT-ATP6 and MT-ATP8 subunits are in orange and blue, respectively. The Pro12 (in human and S.cerevisiae) is highlighted in red, and the yeast Ser46 (Pro66 in human) is in green. F: Cross-species protein conservation of MT-ATP6, flanking the altered proline amino acid. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)