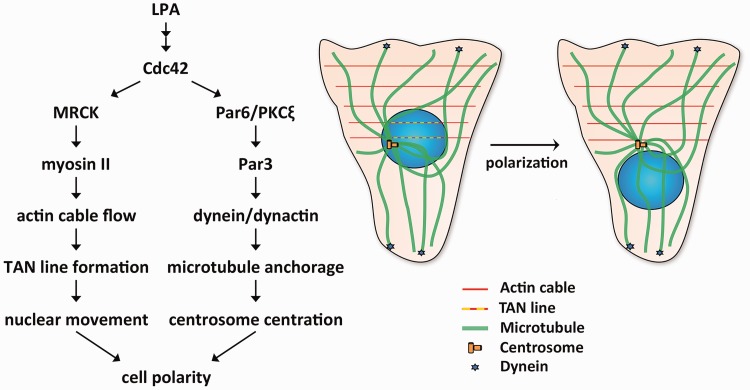
Figure 4.
Mechanisms that generate cell polarity in wounded monolayers of fibroblasts. LPA-treatment of wounded monolayers leads to activation of Cdc42. Cdc42 activates two pathways that lead to cell polarity. In the nuclear movement pathway (left arm of diagram at left), Cdc42 activates myotonic dystrophy kinase-related Cdc42-binding kinase (MRCK), which phosphorylates and activates myosin II, leading to actin cable flow and TAN line formation to move the nucleus. Cdc42 simultaneously activates a second centrosome centration pathway (right arm in the diagram at left), which involves Par6/PKCζ, Par3, dynein/dynactin, and microtubules and holds the centrosome in the centroid of the cell. The schematic diagram at the right shows microtubules, actin cables, TAN lines, and dynein during cell polarization. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)