FIG 8.
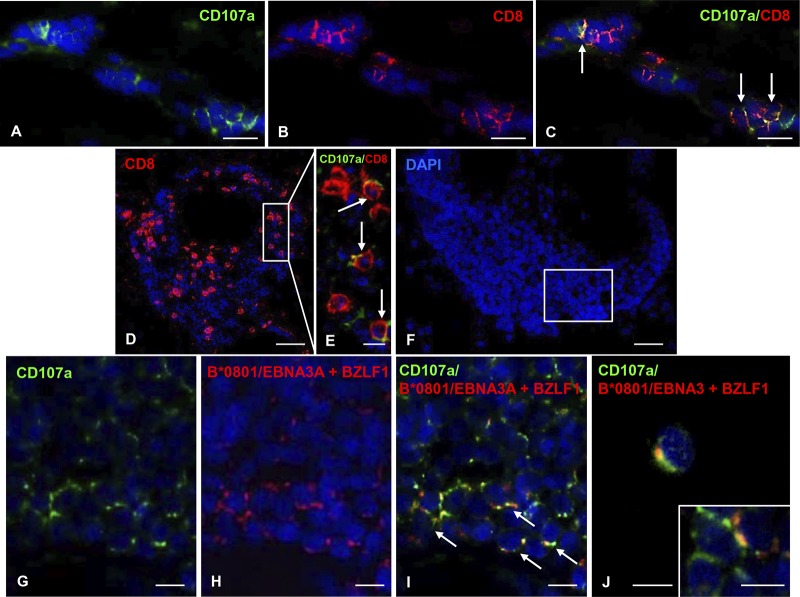
Cytotoxic activity of MS brain-infiltrating EBV-specific CD8 T cells. Double immunofluorescence staining of MS brain sections with MAb to the degranulation marker CD107a (A, green) and polyclonal Ab to CD8 (B, red) reveals the presence of a subpopulation of CD107a+/CD8+ cells among perivascular CD8+ T cells in an active WM lesion of a B*0801+ MS180 donor (C, arrows). (D and E) CD8 T cells (D), some of which coexpress CD107a (E, arrows; the area marked by the frame in panel D is shown at high-power magnification) in a large perivascular cuff, in an active WM lesion of the B*0801+ MS121 donor. (F) DAPI nuclear staining of a large perivascular cuff in an active WM lesion of the B*0801+ MS121 donor. (G to I) Double immunofluorescence staining with anti-CD107a MAb (G, green) and pooled B*0801/EBNA3A and B*0801/BZLF1 pentamers (H, red) reveals presence of CD107a+ pentamer-binding cells (I, arrows) in an area of the perivascular cuff shown in panel F. Two CD107a+ pentamer-binding cells in a different area of the same perivascular cuff are shown in panels J and the inset. Serial sections were used for the stainings shown in panels F to J and in Fig. 2C to F; note that in Fig. 2E and F several BZLF1 pentamer-binding cells are visualized in bright field in the same B-cell-rich cuff. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Bars, 50 μm (D), 20 μm (A to C and F), and 10 μm (E, G to J, and inset in panel J).