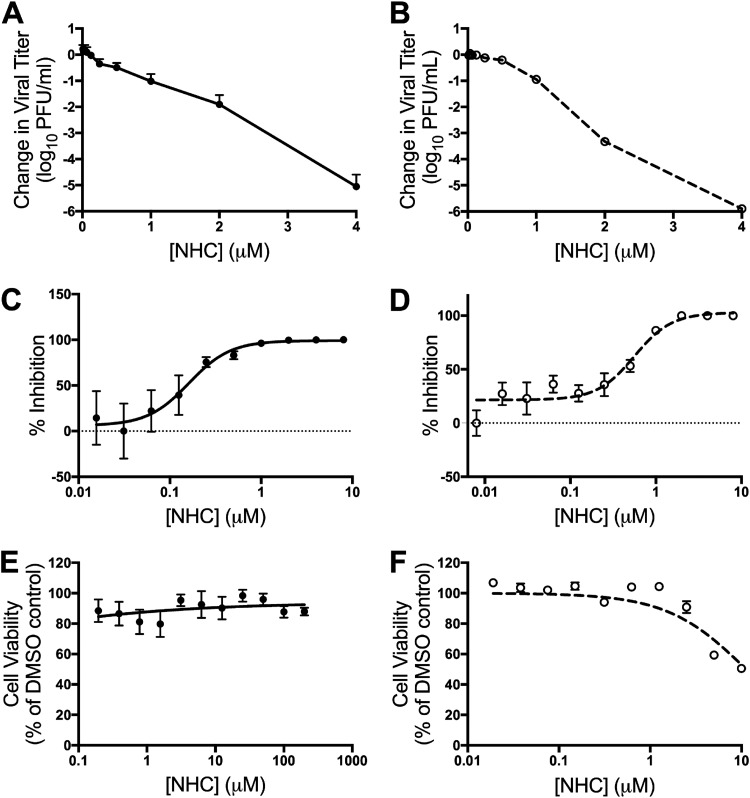
FIG 2.
NHC inhibits MHV and MERS-CoV with minimal cytotoxicity. (A and B) Changes in MHV (A) and MERS-CoV (B) titers relative to vehicle control after treatment with increasing concentrations of NHC. The data represent the results of 6 independent experiments, each with 3 replicates. The error bars represent standard errors of the mean (SEM). (C) Changes in titer data from panel A, represented as percentages of that of vehicle control. WT MHV, EC50 = 0.17 μM. (D) Changes in titer data from panel B, represented as percentages of that of vehicle control. WT MERS-CoV, EC50 = 0.56 μM. (E) DBT-9 cell viability as a percentage of that of DMSO control across NHC concentrations. No cytotoxicity was detected up to 200 μM. The data represent the results of 2 independent experiments, each with 2 replicates (MHV). The error bars represent SEM. (F) Vero cell viability as a percentage of that of DMSO control across NHC concentrations. Less than 50% cytotoxicity was detected up to 10 μM. The data represent the results of 2 independent experiments, each with 3 replicates. The error bars represent SEM.