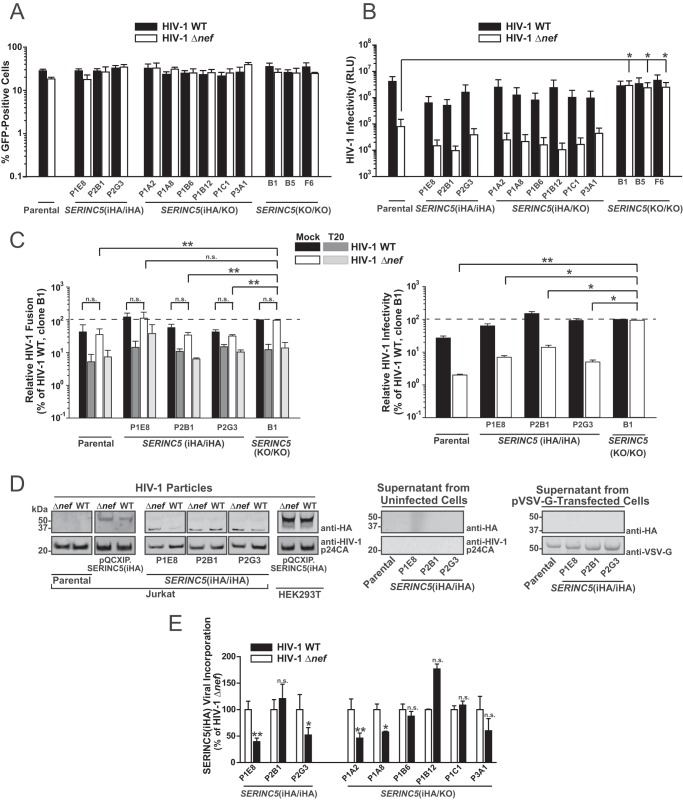
FIG 4.
HIV-1 Nef-mediated enhancement of particle infectivity may occur in the absence of exclusion of endogenous SERINC5 from virions. (A) Parental Jurkat T cells and the indicated clones were infected with VSV-G-pseudotyped HIV-1 WT IRES-GFP and HIV-1 Δnef IRES-GFP. At 2 days postinfection, cells were analyzed for GFP expression by flow cytometry. Error bars indicate SEM from three independent experiments. (B) Infectivity of virions secreted from infected cells (shown in panel A) was analyzed in a luminometric TZM-bl infectivity assay. Shown are SEM from three independent experiments (corresponding to the data in panel A). RLU, relative luminescence units. (C) Parental cells, the indicated SERINC5(HA/HA) clones, and SERINC5(KO/KO) clone B1 were electroporated with a plasmid encoding the β-lactamase-Vpr chimeric fusion protein (pBlaM-Vpr) and proviral plasmids encoding WT HIV-1 or the HIV-1 Δnef mutant. Concentrated virus-containing supernatants were added, in the presence or absence of the HIV-1 fusion inhibitor T-20, to TZM-bl cells, and fusion was quantified as the change in the fluorescence emission of the cell-permeable CCF2 substrate upon cleavage by BlaM-Vpr by flow cytometry. (Left) Relative HIV-1 fusion, normalized to that of WT HIV-1, of clone B1; (right) corresponding relative HIV-1 infectivity. Shown are SEM from two to three independent experiments. (D) Concentrated supernatants from infected, uninfected, and pVSV-G-transfected cells were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) Relative levels of HIV-1 p24-associated SERINC5(iHA) protein were quantified by Odyssey infrared-based imaging. Shown are SEM from three independent experiments.