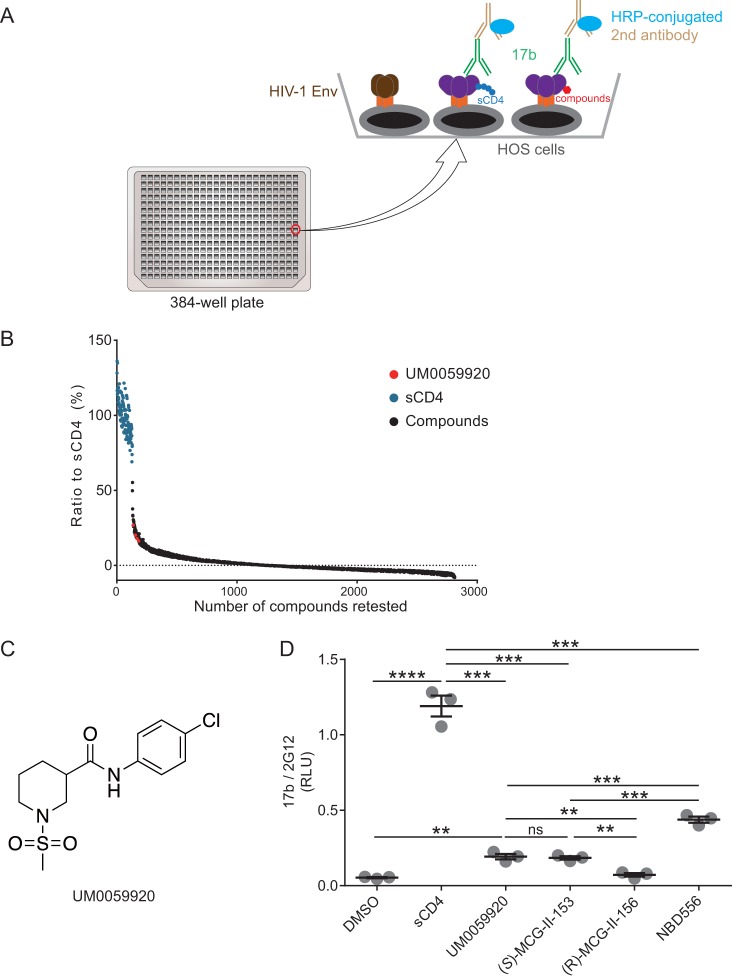
FIG 1.
High-throughput screening of small molecules for their ability to expose the coreceptor binding site. (A) A cell-based ELISA (CBE) was adapted to screen a library comprising ∼108,000 small molecules. In the assay, HOS cells expressing HIV-1JR-FL EnvΔCT were plated in a 384-well-plate format. Small molecules or, as a positive control, sCD4 were added to expose the HIV-1JR-FL EnvΔCT epitope that can be recognized by the CD4i antibody 17b. 17b binding was detected by a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated second antibody, and HRP enzyme activity was measured by Western Lightning oxidizing and luminal reagents. (B) 17b binding in the presence of sCD4 was set as the control, small molecules that enhanced 17b binding above 25% of the one induced by sCD4 were retested in quadruplicate, and only one molecule (UM0059920) was deemed a true positive. (C) UM0059920 is a racemic mixture. (D) Addition of (S)-MCG-II-153 but not (R)-MCG-II-156 enhances 17b binding to levels similar to those of UM0059920 in the CBE. Data shown are mean relative light unit (RLU) values ± standard deviations (SD) from three independent experiments performed in quadruplicate, with the signal obtained from wells transfected with an empty pcDNA3.1 plasmid (no Env) subtracted, normalized to Env levels as determined by 2G12 binding. Statistical significance was evaluated by using an unpaired t test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant).