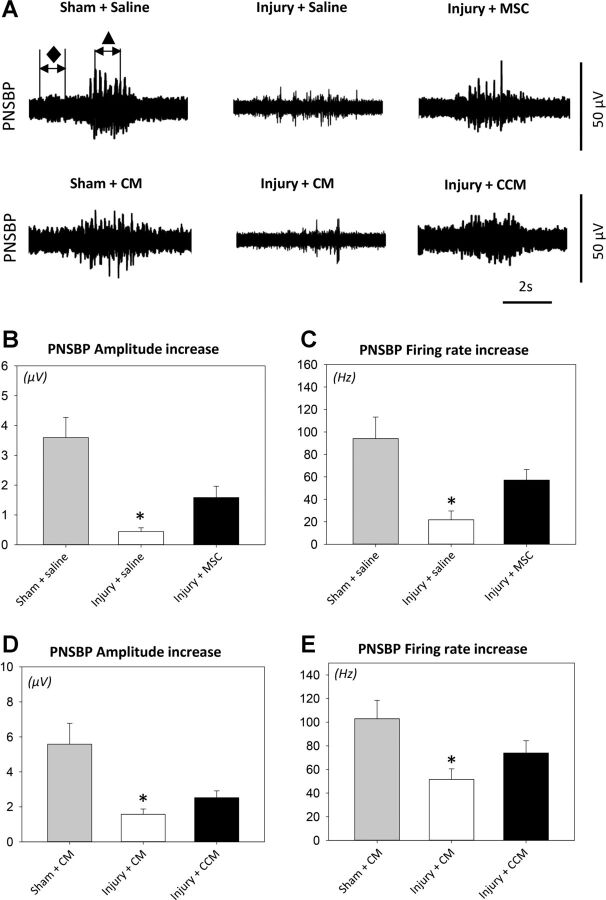
Fig. 2.
Pudendal nerve sensory branch potential (PNSBP) results. Examples demonstrate the two 1-s segments selected from baseline (⧫) and brush activity (▲) that were used to calculate PNSBP amplitude difference (μV) and firing rate difference (Hz) during brush stimuli to the rat clitoris (A). Shown are PNSBP amplitude increase after pudendal nerve crush and vaginal distension (injury) or sham injury with MSC or saline treatment (B) as well as with CCM or CM treatment (D) and firing rate increase after injury or sham injury with MSC or saline treatment (C) as well as with CCM or CM treatment (E). Values are means± SE of data from 8–14 animals. ⧫, Baseline PNSBP; ▲, brush PNSBP. *Significant difference compared with corresponding sham-injured animals, P < 0.05.