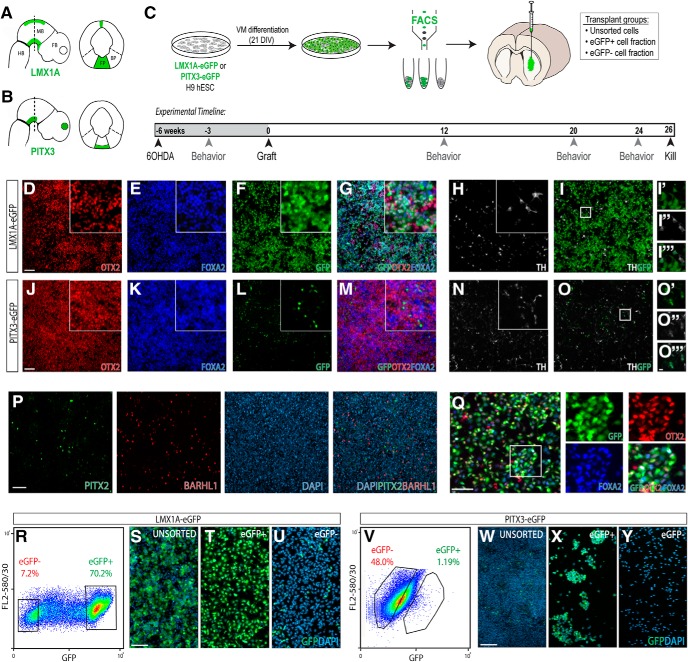
Figure 1.
In vitro differentiation and purification of vm progenitors/precursors using LMX1A-eGFP and PITX3-eGFP human ESC reporter lines. A, B, Schematic coronal and sagittal views of the developing embryo depicting expression patterns of two key vmDA determinant transcription factors: (A) LMX1A and (B) PITX3. eGFP was expressed under the promoter for these two transgenes within H9 hESC lines for the purpose of cell sorting. C, Schematic detailing the differentiation, isolation, and transplantation of cells derived from LMX1A-eGFP and PITX3-eGFP hESC reporter lines, and the experimental timeline for in vivo procedures. D–G, J–M, Validation of efficient vm differentiation by coexpression of OTX2, FOXA2, and eGFP demonstrated robust specification of vm progenitors by 21 DIV. I, O, Maturing dopamine neurons present within the culture at 21 DIV tightly overlapped with eGFP expression. P, Low proportion of PITX2+ and BARHL1+ cells confirmed that cultures were not of unintended subthalamic identity. Q, Immunohistochemical labeling of LMX1A-GFP+ progenitors, 6 h after sorting and replating, showing coexpression of cardinal vmDA progenitor markers OTX2, FOXA2, and LMX1A-GFP. R, V, Flow cytometric plots illustrating the gating for enrichment of eGFP+ and eGFP− populations within differentiating cultures at 21 DIV. Successful isolation of specified populations (unsorted, GFP+, and GFP−) from the (S–U) LMX1A-eGFP and (W–Y) PITX3-eGFP hPSC line was confirmed by replating of cells and immunohistochemical staining for GFP and DAPI. hESC, Human ESCs. Scale bars: D–O, S–U, W–Y, 200 μm; I′–I‴, O′–O‴, 20 μm.