Figure 2.
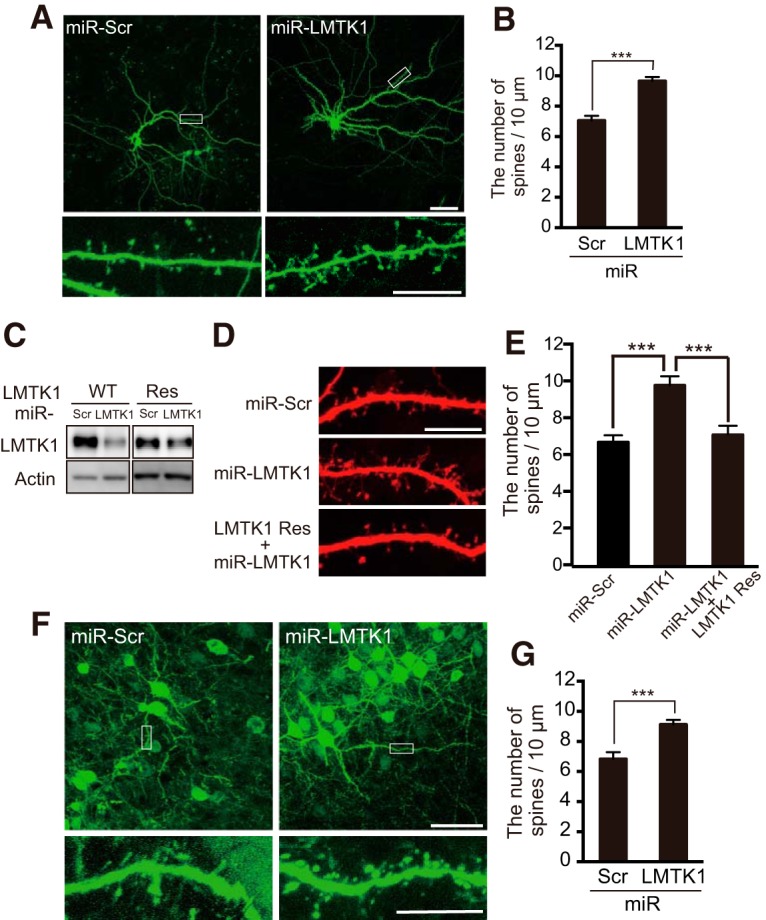
Knockdown of LMTK1 increases the density of dendritic spines in primary cultured neurons and in vivo in developing mouse brains. A, Dendritic spines of LMTK1-knocked down neurons in culture. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with GFP and miR-LMTK1 or miR-Scramble (Scr) at 7 DIV, and dendritic spines were observed at 18 DIV. Bottom, Higher magnification of the white box in the top. Scale bars: top, 50 μm; bottom, 10 μm. B, The density of spines was measured and expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 21 for miR-Scr; n = 34 for miR-LMTK1). C, An immunoblot of LMTK1 WT and LMTK1A Res (miR-LMTK1-resistant LMTK1A) cotransfected into HEK293 cells with miR-LMTK1 or miR-Scr (Scr). Actin is the loading control. D, Dendritic spines of hippocampal neurons transfected with miR-Scr, miR-LMTK1, or LMTK1A Res and miR-LMTK1. E, The density of spines was measured and expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 10 for miR-Scr; n = 10 for miR-LMTK1, n = 13, for LMTK1 Res and miR-LMTK1). F, Neural progenitors were transfected with GFP and miR-LMTK1 or miR-Scr at embryonic day 14 (E14) by in utero electroporation, and dendritic spines were observed at postnatal day 20 (P20). Bottom, Higher magnification of the box indicated in top. Scale bars: top, 50 μm; bottom, 10 μm. G, The density of spines is indicated as mean ± SEM (n = 12 for miR-Scr; n = 33 for miR-LMTK1). ***p < 0.001.
