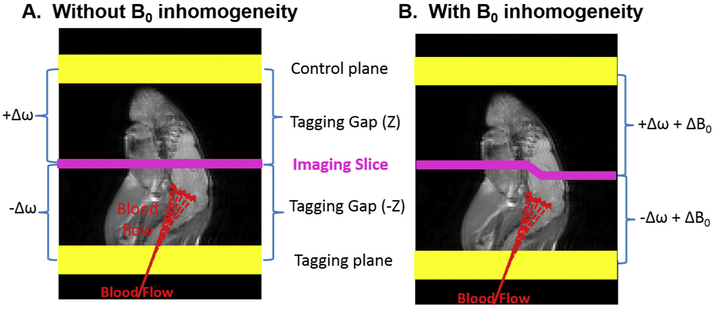
Fig. 1.
The concept of conventional ASL. A) Conventional ASL contrast relies on the signal difference between images with and without the signal from the blood water inverted/saturated. The image with the blood water inverted/saturated, called the tag image, is acquired after inverting/saturating the blood water spins in the arteries prior to entering the imaging plane. Typically, a control image is acquired by tagging a plane located with equal distance but opposite direction from the imaging slice. The conventional ASL MRI works only when there is no static magnetic field (B0) inhomogeneity. B) Under B0 inhomogeneity, tagging offset frequencies of the control plane is not equivalent to that of the tagging plane, leading to B0-inhomogeneity induced artifacts in the resulting CBF maps.