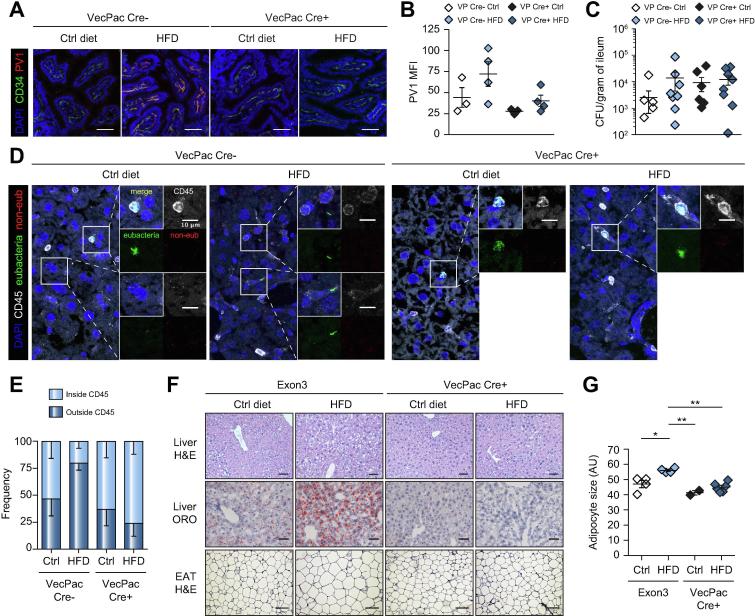
Fig. 4.
Endothelium-specific gain-of-function mice are resistant to steatosis induction. (A–E) β-catenin gain-of-function mice were fed for 2 days with tamoxifen to induce recombination, before being fed with either Ctrl diet or HFD for 1 week or (F,G) 18 weeks. (A,B) Ileum sections were analyzed for the expression of PV1, scale bar indicates 50 µm; and (C) CFUs were determined. (D,E) Liver sections were submitted to eubacteria (green) and non-eub (red) FISH hybridization before CD45 (white) and DAPI (blue) staining. Side images show merged and individual staining of enlarged areas demarcated by squares in the main picture, scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bacteria were enumerated for each mouse, and (E) the percentage of bacteria inside or outside CD45+ cells was determined. (F) After 18 weeks of feeding, EAT and liver sections were analyzed by H&E or ORO staining, as indicated. First row, liver hematoxylin and eosin staining, scale bar indicates 100 µm; second row, liver ORO staining, scale bar indicates 50 µm; third row EAT hematoxylin and eosin staining, scale bar indicates 50 µm. Adipocyte diameter was measured and displayed in G. *p <0.05; **p <0.005; Bonferroni 1-way ANOVA. CFUs, colony-forming units; EAT, epididymal adipose tissue; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; HFD, high-fat diet; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ORO, Oil Red O.