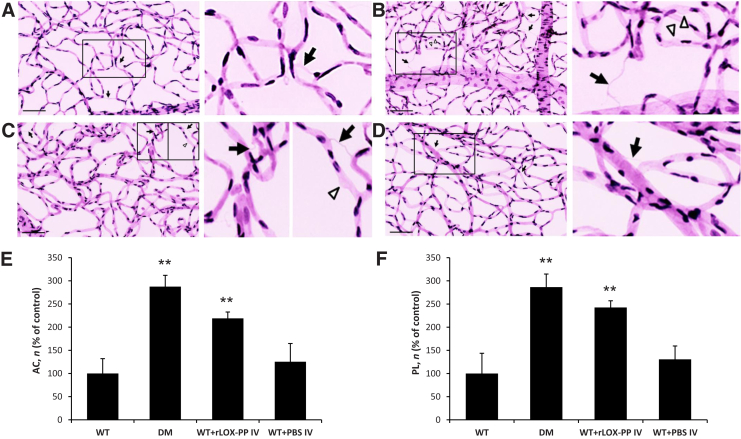
Figure 6.
Effect of recombinant lysyl oxidase propeptide (rLOX-PP) on the development of acellular capillaries (ACs) and pericyte loss (PL) in rat retinas. A–D: Representative retinal trypsin digest images showing retinal vascular networks of a control rat (A, left panel), diabetic (DM) rat (B, left panel), rat intravitreally injected with rLOX-PP (C, left panel), and rat intravitreally injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (D, left panel). LOX-PP administration promoted the development of ACs (arrows) and PL (arrowheads) associated with diabetic retinopathy. Boxed areas are shown at higher magnification in the right column. E and F: Graphical illustration of cumulative data of the number of ACs (E) and PL (F) in four groups of rats: wild-type (WT), diabetic (DM), WT intravitreally injected with rLOX-PP (WT+rLOX-PP IV), and WT intravitreally injected with PBS (WT+PBS IV). Administration of rLOX-PP alone promoted the development of ACs and PL in rat retinas. **P < 0.01 versus WT. Scale bar = 100 μm.