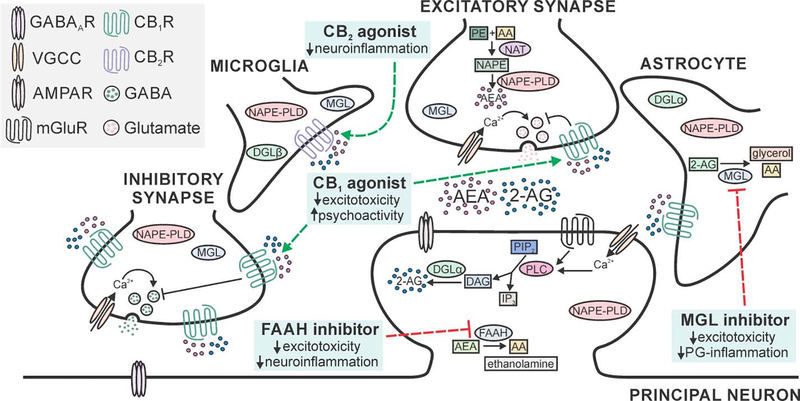
Fig. 1:
Neuroprotective targets in the eCB system. Schematic displays principal neuron receiving excitatory and inhibitory input with neighboring astrocyte and microglial cells. Cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1Rs) are present on presynaptic terminals, with high expression on a subset of GABAergic terminals and widespread expression at lower levels on glutamatergic terminals (Marsicano and Lutz, 1999). Cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2Rs) are found predominantly on cells of the immune system (microglia shown), with limited expression on neurons (not shown) (Nunez et al., 2004). All four cell types express diacylglycerol lipase (DGL) and N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD), the enzymes that synthesize the eCBs 2-arachdionoylglycerol (2-AG) and anandamide (AEA), respectively (Egertova et al., 2008; Ludanyi et al., 2011; Mishra et al., 2016; Viader et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2011). For clarity, the pathways are described in detail in a single location with high expression. 2-AG is hydrolyzed by monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) that is expressed in all four cell types, with the highest levels found in astrocytes (Muccioli et al., 2007; Viader et al., 2015). Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is predominantly expressed in the somata and dendrites of principal neurons (Egertova et al., 2003; Tsou et al., 1998b). Important neuroprotective drug targets (blue boxes) include agonists for CB1 and CB2Rs (dashed green lines) and inhibitors of MGL and FAAH (dashed red lines). Abbreviations; 2-AG: 2-arachidonoylglycerol; AMPAR: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; AA: arachidonic acid; AEA: arachidonoyl ethanolamine (anandamide); CB1R: cannabinoid type 1 receptor; CB2R: cannabinoid type 2 receptor; DAG: diacylglycerol; DGL: diacylglycerol lipase; FAAH: fatty acid amide hydrolase; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; GABAAR: GABA type A receptor; IP3: inositol triphosphate; mGluR: metabotropic glutamate receptor; MGL: monoacylglycerol lipase; NAPE-PLD: N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D; NAT: N-acyltransferase; NAPE: N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine; PE: phosphatidylethanolamine; PG: prostaglandin; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PLC: phospholipase C; VGCC: voltage-gated Ca2+ channel.