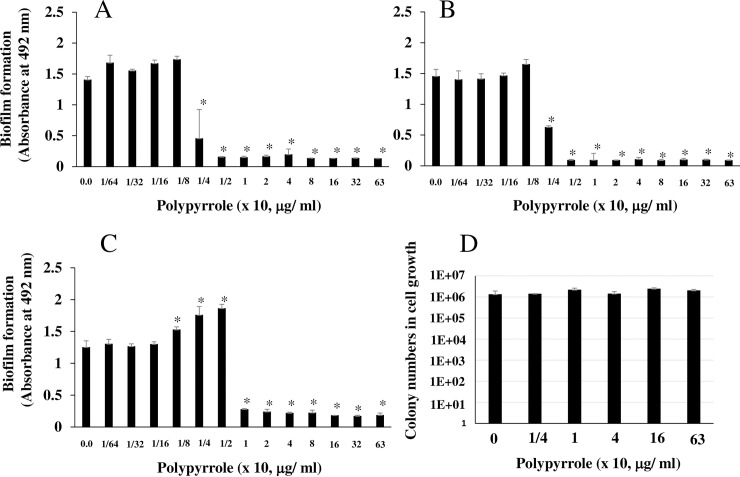
Fig 5. Biofilm formation by S. sanguinis induced by polypyrrole.
The effects of polypyrrole on the biofilm formation of S. sanguinis were observed. Biofilm formation by S. sanguinis ATCC 10556 was quantitatively assessed with various concentrations of polypyrrole on human saliva-coated (A)-, uncoated (B), and BSA-coated (C) 96-well microtiter plates in TSB supplemented with 0.25% sucrose, including various concentrations of polypyrrole. (D) The growth of S. sanguinis was assessed by measuring the cell colonization numbers on BHI agar plates after 16 h of incubation in TSB supplemented with 0.25% sucrose, including various concentrations of polypyrrole. Small C indicated no polypyrrole as a control. The data indicated the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. The independent experiments were performed 3 times, with similar results obtained in each. The asterisks indicated a statistically significant difference among multiple groups (ANOVA with Bonferroni correction; p-values < 0.05, various concentrations of polypyrrole vs no polypyrrole control).