Fig 3. Hippocampal HIV-1 Nef expression decreases ileal tissue thickness and villi area and induces highly reactive follicular hyperplasia.
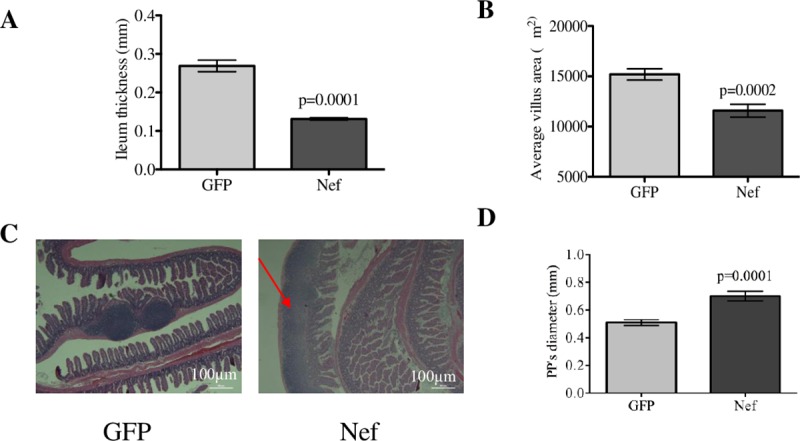
(A) Measurements of intestinal thickness with a caliper showed that ileal tissue from Nef-treated rats was significantly thinner than that of the GFP-treated rats. (B) Analysis of the villi area showed that the intestinal villi from HIV-1 Nef-treated rats were significantly smaller compared to those of the GFP-treated rats. (C) H&E staining of the ileum showed lymphoid hyperplasia (expansion of Peyer’s patches, red arrow) in Nef-treated animals in comparison to normal Peyer’s patches in controls. Scale bars indicate 0.5 mm. (D) The microscopic diameters of the Peyer’s patches (PPs) show that PPs from Nef-treated rats are significantly increased compared to those in the GFP-treated rats, confirming that HIV-1 Nef expression in the hippocampus induces highly reactive follicular hyperplasia in the intestines. N = 4 to 9 rats per group. Student’s t-test was performed to determine differences between the Nef-treated group and the GFP-treated group (control). Error bars indicate means ± S.E.M.
