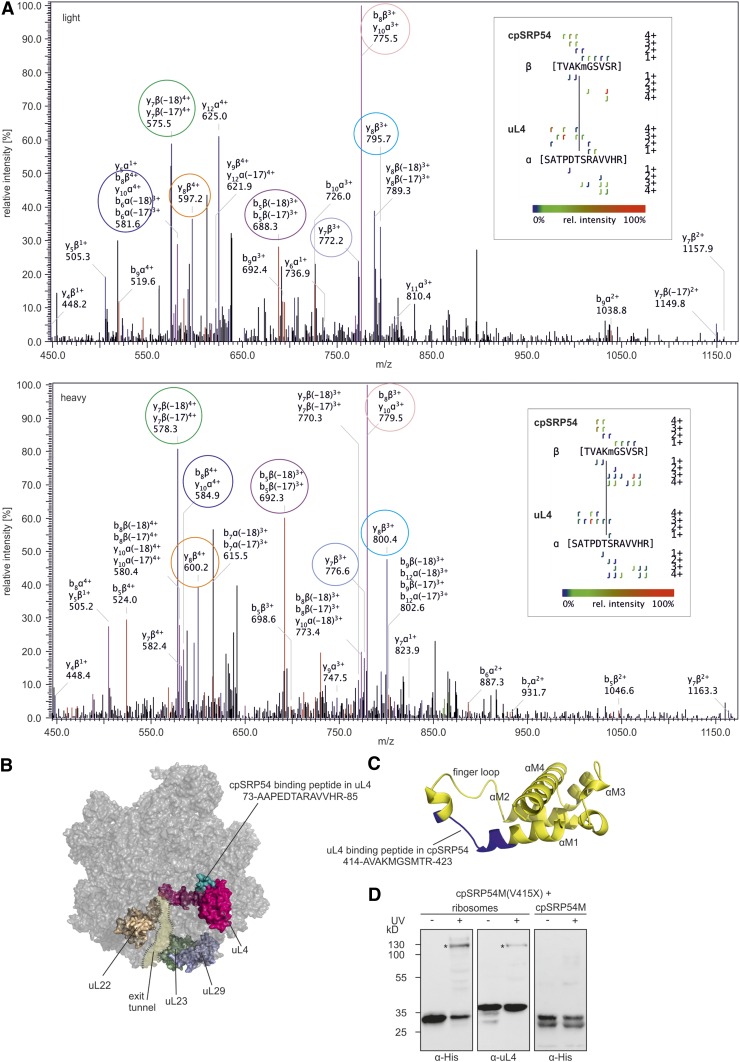
Figure 6.
Identification of Crosslinks between cpSRP54 and uL4.
(A) Fragmentation pattern of the crosslink. Chloroplast ribosomes of P. sativum were incubated with isotope-coded BS3 (1:1 mixture of H12-BS3 and D12-BS3). The sample was analyzed via liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Assigned b-ions are depicted in red, y-ions in blue, and nonidentified ions in black. Ions that can be assigned to both b- and y-ions are depicted in pink. Fragment ion pairs of the light and heavy form that show the characteristic mass shift of 12 D are encircled in the same color. The crosslinked peptide-fragment is shown on the right side of each spectrum.
(B) Ribosomal location of uL4 (pink) and the cpSRP54 binding peptide in uL4 (green) is visualized using the cryoelectron microscopy structure of the 50S large subunit of the spinach chloroplast ribosome (PDB: 5X8T). Ribosomal proteins that form the exit tunnel or the tunnel exit point are depicted in brown (uL22), light green (uL23), and light blue (uL29).
(C) Location of the uL4 binding peptide (blue) in a homology model of cpSRP54M (yellow). The homology model was generated using the Phyre2 web portal (Kelley et al. 2015) and the signal sequence binding subunit of Ffh from T. aquaticus (PDB: 2FFH) as template.
(D) Recombinant cpSRP54M-His(V415X) containing the UV light-inducible crosslinker pBpa (X) was incubated with chloroplast ribosomes or His-cpSRP54M in the absence (−) or presence (+) of UV light. The assay was analyzed immunologically using antibodies against the His-Tag (α-His) and the ribosomal protein uL4 (α-uL4). Specific crosslinking products are indicated with an asterisk (*).