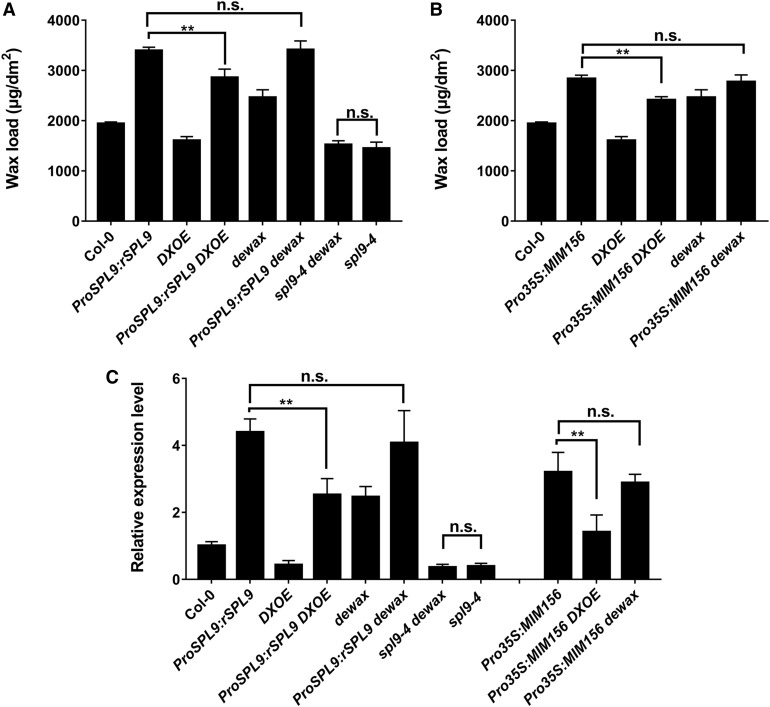
Figure 8.
SPL9 Acts Downstream of DEWAX in Wax Synthesis.
(A) Genetic relationship analysis of SPL9 and DEWAX in wax synthesis with double mutant phenotype analysis. Cuticular wax amounts of inflorescence stems from 6-week-old double mutants between Pro35S:rSPL9, spl9-4, dewax, and DXOE grown in long-day conditions were examined by GC-FID. Wax coverage is expressed as wax amounts per stem surface area (μg.dm-2). Error bars indicate ±sd (**P < 0.01, Student’s t test) from four replicate experiments; n.s. represents no significant difference.
(B) Genetic relationship analysis of miR156 and DEWAX in wax synthesis with double mutant phenotype analysis. Cuticular wax amounts of inflorescence stems from 6-week-old double mutants between Pro35S:MIM156 and dewax or DXOE grown in long-day conditions were examined by GC-FID. Wax coverage is expressed as wax amounts per stem surface area (μg.dm-2). Error bars indicate ±sd (**P < 0.01, Student’s t test) from four replicate experiments; n.s. represents no significant difference.
(C) RT-qPCR analysis of CER1 expression in the indicated mutants. Expression was normalized relative to that of PP2A. Expression level in the wild type (WT) was set as 1. Each column represents the mean of three independent assays, and the error bars indicate ±sd (**P < 0.01, Student’s t test); n.s. represents no significant difference.