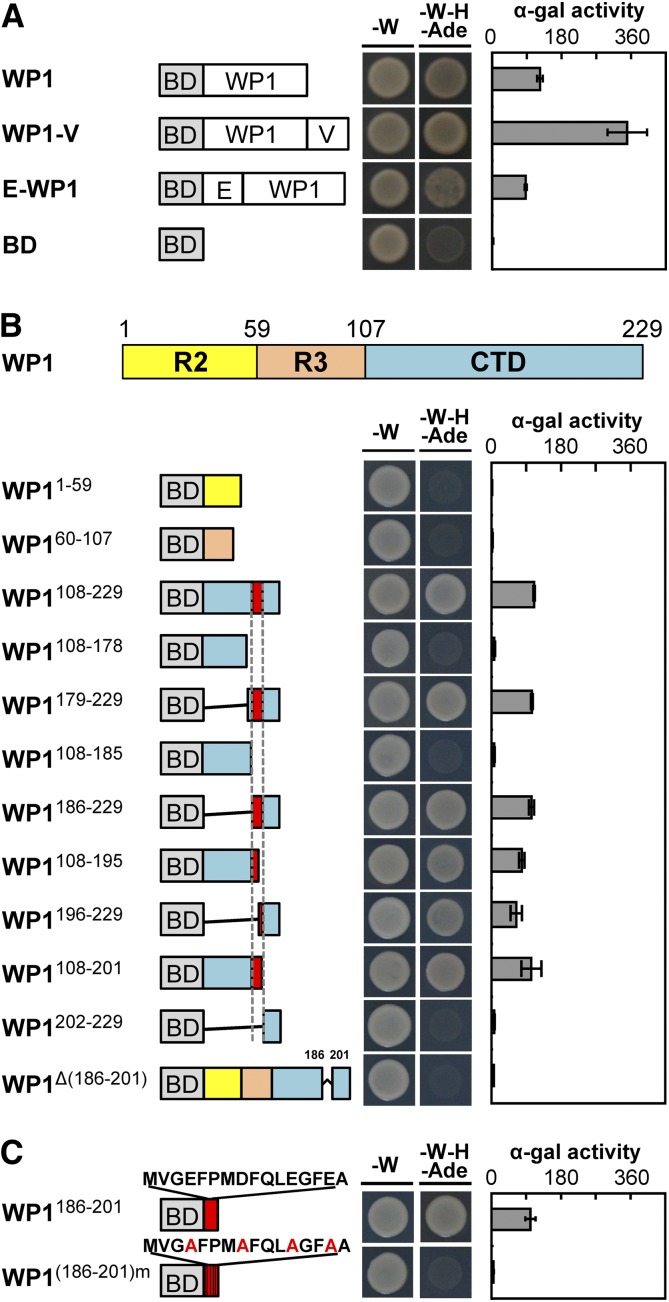
Figure 4.
WP1 Acts as a Transcriptional Activator.
(A) Transactivation analysis of WP1, WP1-VP64, and EAR4-WP1 using a yeast assay. VP64 and EAR4 are an exogenous activation domain and an exogenous repression module, respectively. The GAL4 DNA BD alone was used as the negative control. Plate auxotroph and α-galactosidase assay showing transcriptional activation of each protein. Bars represent means ± sd of three independent experiments. α-gal, α-galactosidase; E, EAR4; V, VP64; -W, SD/−Trp; -W-H-Ade, SD/−Trp/−His/−Ade.
(B) Mapping of the transactivation motif of WP1 using a yeast assay. R2, amino acids 1 to 59; R3, amino acids 60 to 107; CTD, amino acids 108 to 229. Plate auxotroph and α-galactosidase assay showing transcriptional activation of each protein. Bars represent means ± sd of three independent experiments. α-gal, α-galactosidase; BD, GAL4 DNA binding domain; -W, SD/−Trp; -W-H-Ade, SD/−Trp/−His/−Ade.
(C) Transactivation analysis of the C-terminal motif MVGEFPMDFQLEGFEA using a yeast assay. BD stands for the GAL4 DNA binding domain. Mutations introduced into the C-terminal motif are indicated by red font. Plate auxotroph and α-galactosidase (α-gal) assay showing transcriptional activation by each protein. Bars represent means ±sd of three independent experiments. α-gal, α-galactosidase; -W, SD/−Trp; -W-H-Ade, SD/−Trp/−His/−Ade.