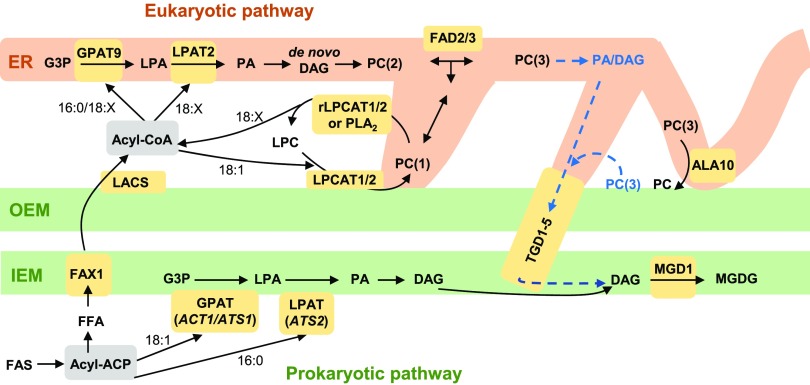
Figure 12.
Updated Model of Wild-Type Arabidopsis Acyl Trafficking within Leaf Glycerolipid Assembly Clarifying the Role of LPCAT1 and LPCAT2.
The model focuses on the trafficking of acyl groups between the chloroplast and the ER for MGDG synthesis. Here the model separates PC involved in acyl editing “PC(1)” from PC synthesized de novo “PC(2)” and PC that provides the substrate for MGDG synthesis “PC(3).” The model also allows that PC acyl editing may take place in the ER or at the chloroplast surface, which could be a way to move acyl groups into the ER by PC movement through membrane contact sites. The PC(3) pool is derived from de novo synthesized PC(2), which may have been further desaturated by FAD2 and FAD3. The substrate for MGDG synthesis may come from turnover of the PC(3) pool in the ER, or turnover of the PC(3) at the chloroplast surface. Key enzymes/transporters are in yellow; uncertain reactions are in blue and have dashed lines. rLPCAT, reverse LPCAT reaction.