Fig. 3. One intravenous HEDGES injection of multicassette DNA vectors encoding cognate mAb heavy- and light-chain cDNAs produce prolonged bioactive mAb serum proteins.
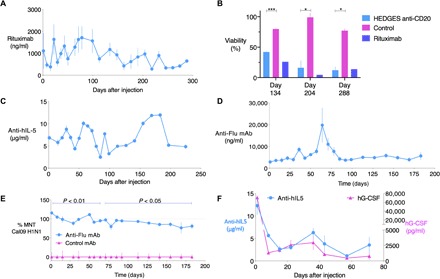
On day 0, groups of CD-1 mice (n = 3) were given dexamethasone intraperitoneally 2 hours before intravenous coinjection of 1120 nmol DOTAP + Dex and 1000 nmol DMPC + Dex liposomes and 2 minutes later intravenously, and then 88 μg of mAb heavy- and light-chain cDNA vector intravenously. Control mice received LRS. (A) Mean ± SEM rituximab serum levels at indicated time points were measured by ELISA. mAb levels in sera from untreated control mice, as well as from mock-treated control mice (mice receiving HEDGES encoding unrelated mAb cDNAs), were undetectable in the rituximab, 5J8 mAb, and mepolizumab ELISAs, respectively. (B) Mean ± SEM viability of CD20+ Raji lymphoma target cells is shown following incubation with human plasma and sera from anti-CD20 or control HEDGES-treated mice isolated at indicated time points. Target Raji cells incubated with recombinant rituximab (10 mg/ml) is also presented for comparison. ***P < 0.001 and *P < 0.05 by ANOVA method. (C) Mean ± SEM anti–IL-5/mepolizumab serum levels are shown over time by ELISA. 5J8 anti-H1 IAV mAb serum levels were measured by ELISA (D) and tested in parallel for capacity to neutralize Cal09 H1N1 IAV in a microneutralization assay (MNT) at indicated time points (E). Serum from HEDGES-rituximab–treated mice (control) served as controls at all time points in ELISA and MNT. (F) Mepolizumab and hG-CSF serum levels over time following intravenous HEDGES injection of an 8.8-kb triple-cassette cDNA vector encoding hG-CSF and mepolizumab heavy- and light-chain cDNAs. Graphs represent mean ± SEM. One representative result from two to three independent experiments is shown.
