Fig. 4. Cohesin and Scc2-Scc4 mediate intermolecular DNA bridges that slide on DNAs.
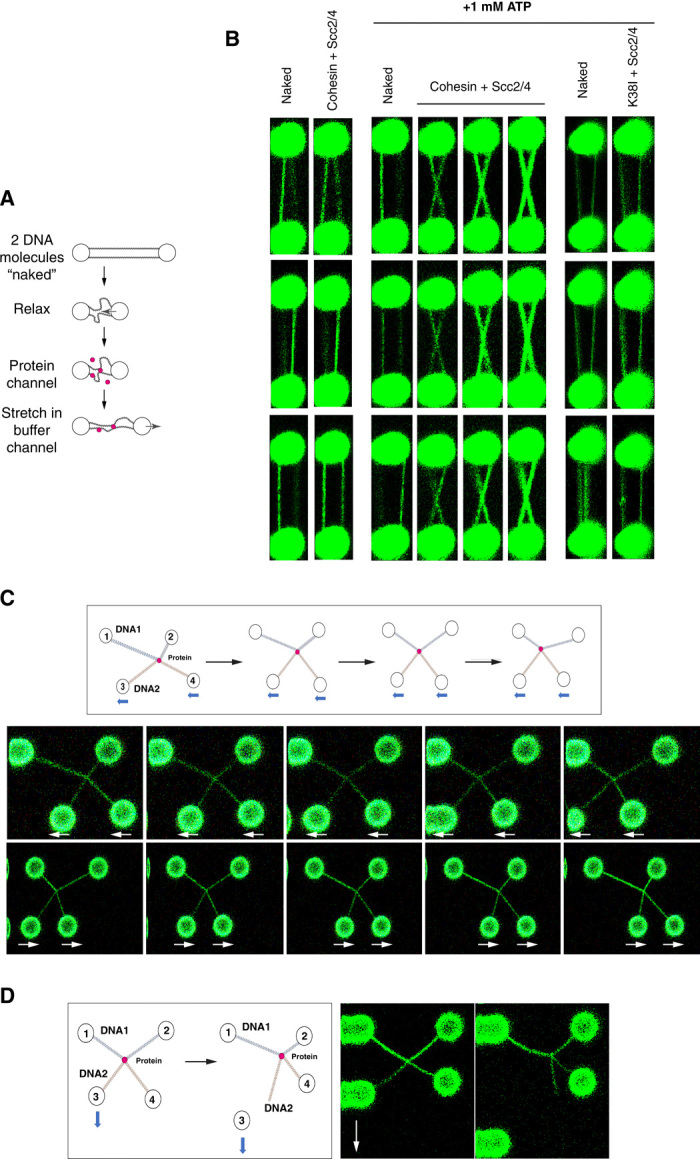
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental design for the dual-trap optical tweezer to generate permanent intermolecular cohesin bridges. Two λ-DNA molecules are tethered between the two beads and incubated in a relaxed position (3-μm bead distance) in the presence or absence of protein in buffer containing 50 mM NaCl. The relaxed molecules are then moved to a different channel containing 300 mM NaCl and reextended. Imaging is done before incubations and after reextension in a buffer containing 300 mM NaCl and 50 nM SYTOX Orange to visualize DNA. (B) Two λ-DNA molecules were tethered and treated as described in (A) and incubated with either (i) 1 nM cohesin, 2.5 nM Scc2-Scc4, and no ATP (Cohesin + Scc2/4, left); (ii) 1 nM cohesin, 2.5 nM Scc2-Scc4, and 1 mM ATP (Cohesin + Scc2/4, middle); or (iii) 1 nM cohesin ATPase mutant K38I, 2.5 nM Scc2-Scc4, and 1 mM ATP (K38I + Scc2/4, right). Imaging was performed before incubation and after DNA reextension in a buffer containing 300 mM NaCl to minimize DNA entanglement and 50 nM SYTOX Orange to visualize DNA. Images from three independent experiments are shown. Three independent experiments are shown for each category. (C) Schematic representation of the experimental design to test for sliding of permanent cohesin bridges (top diagram). Following the formation of an intermolecular cohesin bridge (see fig. S8 for details in bridge formation protocol), beads 3 and 4 were moved together in the x axis to slide the bridge along DNA1. Images showing two representative sliding experiments are shown. Experiments were performed in a buffer containing 300 mM NaCl and 50 nM SYTOX Orange. Movies of the experiments are shown in movies S4 and S5. The experiment was performed three times, and sliding was observed in all cases. (D) Schematic representation of the experimental design to disrupt intermolecular cohesin bridges. Following the formation of an intermolecular cohesin bridge, bead 3 is moved down in the y axis until one of the DNA ends loses contact with the bead. Imaging was performed before and after the pull in a buffer containing 300 mM NaCl and 50 nM SYTOX Orange. Representative experiment is shown. A movie of the experiment is shown in movie S6.
