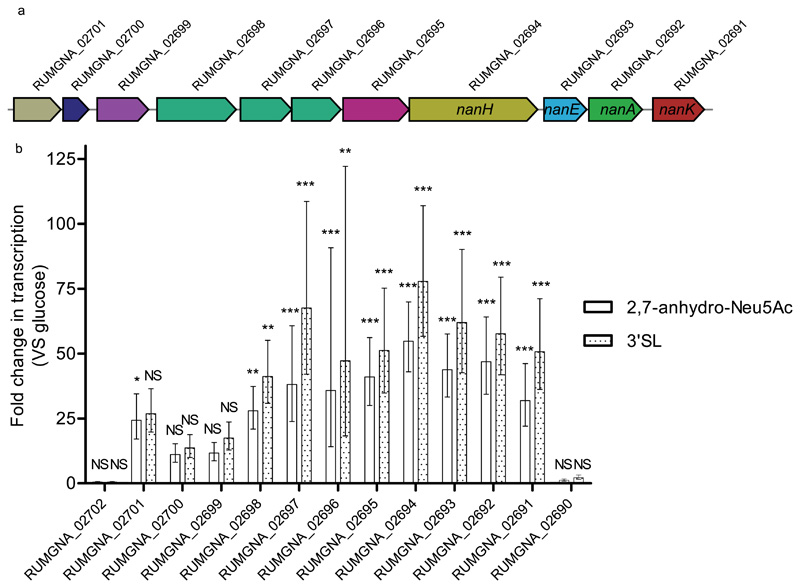
Figure 1. R. gnavus ATCC 29149 nan operon.
a) Diagram depicting the genomic organisation of the nan operon RUMGNA_02701 (putative sialic acid esterase; tan) RUMGNA_02700 (putative YhcH family protein; dark blue), RUMGNA_02699 (predicted transcriptional regulator; purple), RUMGNA_02698 – 02696 (putative sialic acid ABC transporter of the SAT2 family; green), RUMGNA_02695 (putative oxidoreductase, pink), RUMGNA_02694 (RgNanH (Intramolecular trans sialidase), gold), RUMGNA_02693 (NanE (epimerase), blue), RUMGNA_02692 (NanA (aldolase), dark green), RUMGNA_02691 (kinase) (NanK, red). b) qPCR analysis showing fold changes in expression of nan genes when R. gnavus was grown with 3’SL or 2,7-anhydro-Neu5Ac compared to glucose using ΔΔCt calculation. Error represent standard deviation and are based on three biological replicates analysed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined using a 1-way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. NS – no significant change in expression (p > 0.05), * - p 0.05 – 0.01, ** - p 0.01 – 0.001, *** - p < 0.001.