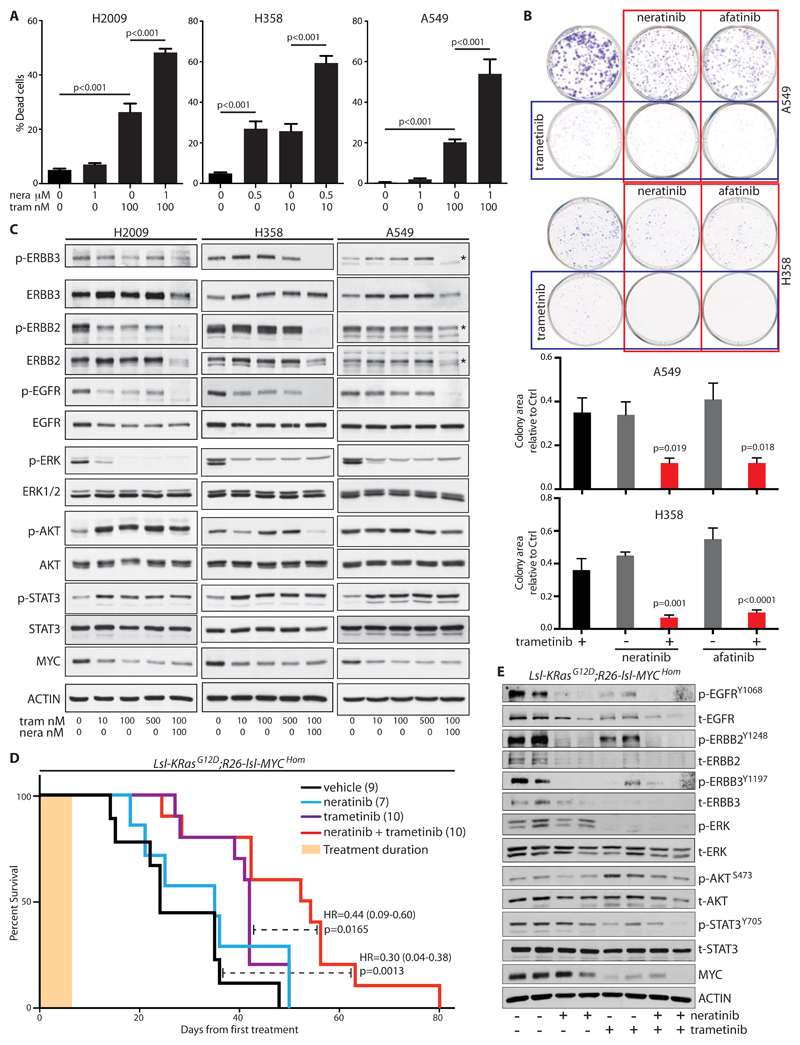
Figure 5. ERBB blockade enhances MEK inhibitor-driven apoptosis in vitro and therapeutic impact in vivo.
A) Apoptosis induced in human NSCLC cells, measured 48 hours after treatment with the indicated doses of neratinib (nera) and/or trametinib (tram). Mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments shown (ANOVA & Tukey test). B) Clonogenic assay showing suppression of colony formation in A549 and H358 cells after 48 hours of treatment with the indicated inhibitors. Lower panels show quantification of colony area (% surface coverage) from 5 independent experiments. Significance was determined for drug combinations versus trametinib alone. (ANOVA & Tukey test). C) Lysates from the indicated cells treated for 24 hours with increasing doses of trametinib alone or the combination of trametinib and neratinib, immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Asterisks, where present, indicate the correct band. D) Overall survival, measured from the first day of treatment, of tumor-bearing KM mice treated daily for 1 week (tan bar) with neratinib (80 mg/kg), trametinib (1 mg/kg), or the combination of both, then followed without further intervention. Treatment was commenced at 5 weeks PI. Cohorts shown are vehicle (n=9); neratinib (n=7); trametinib (n=10); trametinib + neratinib (n=10). Logrank hazard ratios (HR±95% CI) and p values are shown for comparisons of T+N versus vehicle and T+N versus T alone (dashed lines). E) Lysates of individual tumors from mice treated with neratinib (80 mg/kg) and/or trametininb (1 mg/kg) for 3 days, blotted with the indicated antibodies.