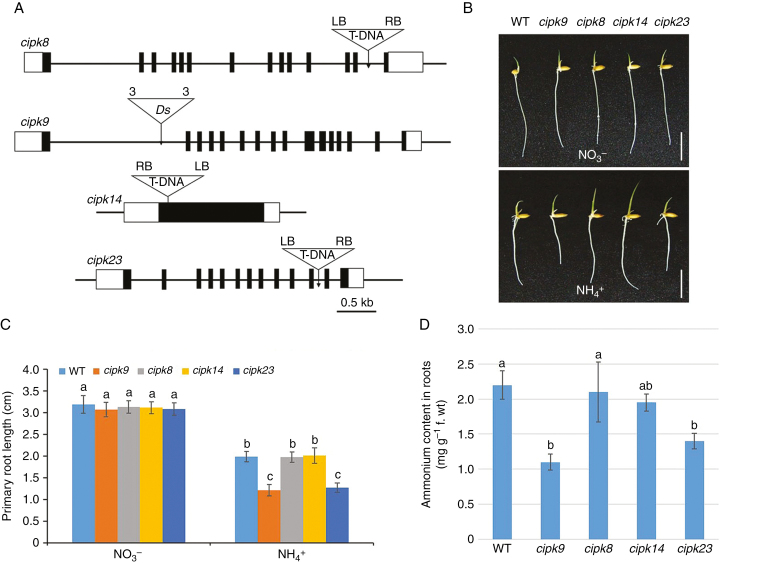
Fig. 6.
Gene structure, root growth and cellular NH4+ content of cipk mutants. (A) Schematic diagrams showing gene structures of the cipk insertion mutants, cipk8, cipk9, cipk14 and cipk23. Black boxes, exons; white boxes, untranslated regions. Triangles indicate T-DNA or Ds insertion sites; ‘3’ and ‘5’ indicate the 3’ and 5’ ends of Ds, respectively; RB, right border of T-DNA; LB, left border of T-DNA. Scale bar = 0.5 kb. (B) Appearances of wild-type (WT), cipk8, cipk9, cipk14 and cipk23 seedlings after 4 d growth in nutrient solution containing either NO3– or NH4+ as the sole N source (Supplementary data Table S1). Scale bar = 1 cm. (C) Primary root lengths of wild-type, cipk8, cipk9, cipk14 and cipk23 seedlings grown as in (B). (D) Cellular NH4+ levels in roots of each line after 4 d growth in nutrient solution containing NH4+ as the sole N source. Data in (C) and (D) are means ± s.e. (n > 10 plants per line); different letters indicate significant differences between results (P < 0.05).