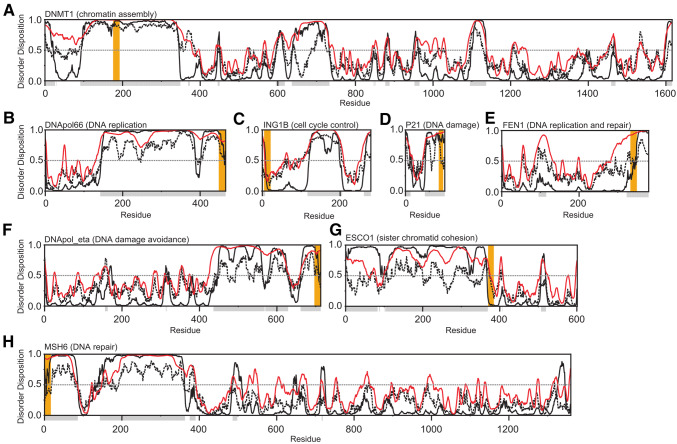
Fig. 3.
PCNA motifs reside predominantly in intrinsically disordered regions. a DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (human)—chromatin assembly. b DNA polymerase δ (human)—DNA replication. c p33 (inhibitor of growth 1b) (human)—cell cycle control. d p21 (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1) (human)—DNA damage. e Flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) (human)—DNA replication and repair. f DNA polymerase η (human)—DNA damage avoidance. gN-acetyltransferase ESCO2 (human)—sister chromatid cohesion. h DNA mismatch repair protein MSH6 (human)—DNA repair. The disorder propensity from 0 to 1 is plotted as a function of residue number and was predicted using Disopred3 (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred) (black), IUpred2 (https://iupred2a.elte.hu) (striped black), and Pondr-fit VSL2 (http://www.pondr.com) (red) and default settings. The disorder for each residue was denoted with gray boxes below the x-axis by calculating the average disorder disposition for the three predictors with a threshold equal to or above 0.5 (indicated by gray dotted line). Orange boxes show PCNA binding motif-locations