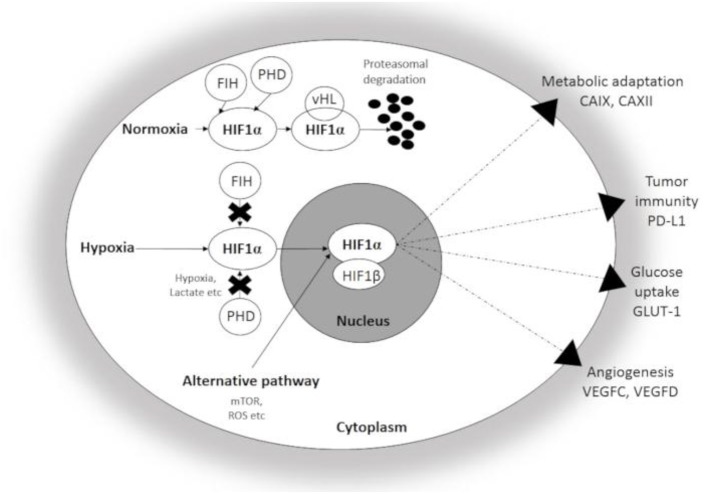
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of Hypoxia Inducible factor 1-α (HIF1α) associated changes in hypoxic conditions. Under normoxia, HIF1α undergoes rapid proteasomal degradation due to the oxygen-dependent modification by PHDs. In contrast, HIF1α is stabilized and translocated into the nucleus under hypoxia, and after dimerization with the β-subunit, the active heterodimer initiates the transcription of hypoxia-responsive genes participating in adaptation. CAIX, CAXII, carbonic anhydrase IX and XII; GLUT-1, Glucose transporter 1; PD-L1, Programmed cell death ligand 1; VEGFC and D, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C and D; FIH, Factor Inhibiting HIF; PHD, Prolyl hydroxylase.