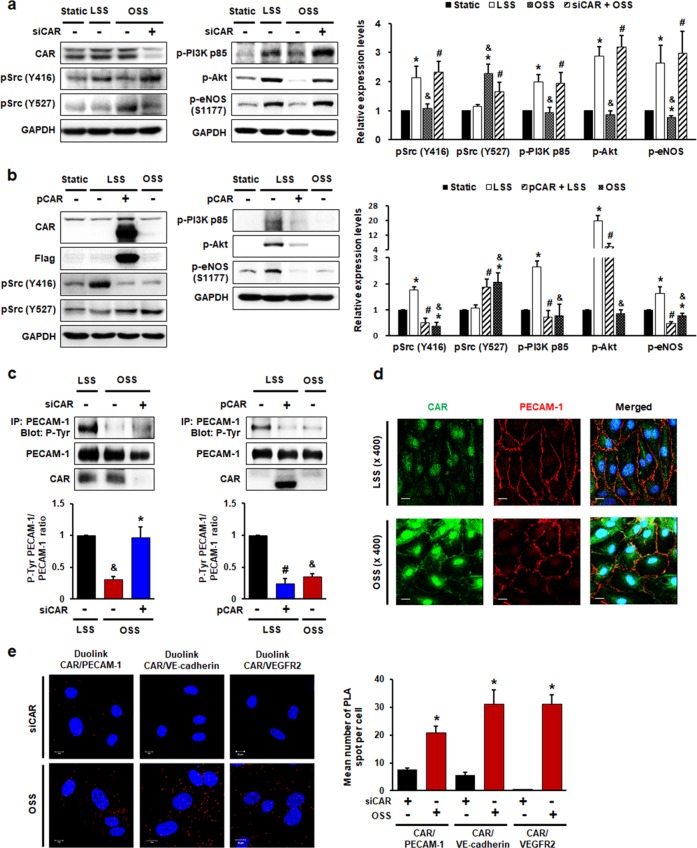
Fig. 5. CAR acts as a mechanotransduction modulator in endothelial cells under disturbed flow.
HUVECs transfected with siRNA (a, c, e) against CAR or flag-tagged plasmid (b, c) encoding CAR were exposed to FSS. The phosphorylation of Src at Y416 (active form) and Y527 (inhibitory form), PI3K, Akt, and eNOS (S1177) was assessed. Representative images from at least five experiments are shown. a n = 5; *P < 0.05, static vs. LSS or OSS; &P < 0.05, LSS vs. OSS; #P < 0.05, OSS vs. siCAR + OSS. b n = 5; *P < 0.05, static vs. LSS or OSS; &P < 0.05, LSS vs. OSS; #P < 0.05, LSS vs. pCAR + LSS. c Transfected HUVECs exposed to FSS for 10 min were immunoprecipitated with anti-PECAM-1 antibody. The tyrosine phosphorylation of PECAM-1 was assessed in PECAM-1 immunoprecipitates by western blotting (n = 5; &P < 0.05, LSS vs. OSS; *P < 0.05, OSS vs. siCAR + OSS; #P < 0.05, LSS vs. pCAR + LSS). d Colocalization of CAR with PECAM-1 was visualized by confocal microscopy. Representative images from at least three experiments are shown (green, CAR; red, PECAM-1; blue, nuclei; scale bars, 10 μm). e The association between CAR and the mechanosensory complex (VEGFR2, VE-cadherin, and PECAM-1) in HUVECs exposed to disturbed flow was determined by PLA. Cells transfected with siCAR were used as a negative control. Red spots indicate interactions between CAR and the mechanosensory complex. Red spots were enumerated to quantify the number of in situ PLA signals per cell. Representative images are shown (n = 5; compared with siCAR, *P < 0.05; scale bars, 10 μm).