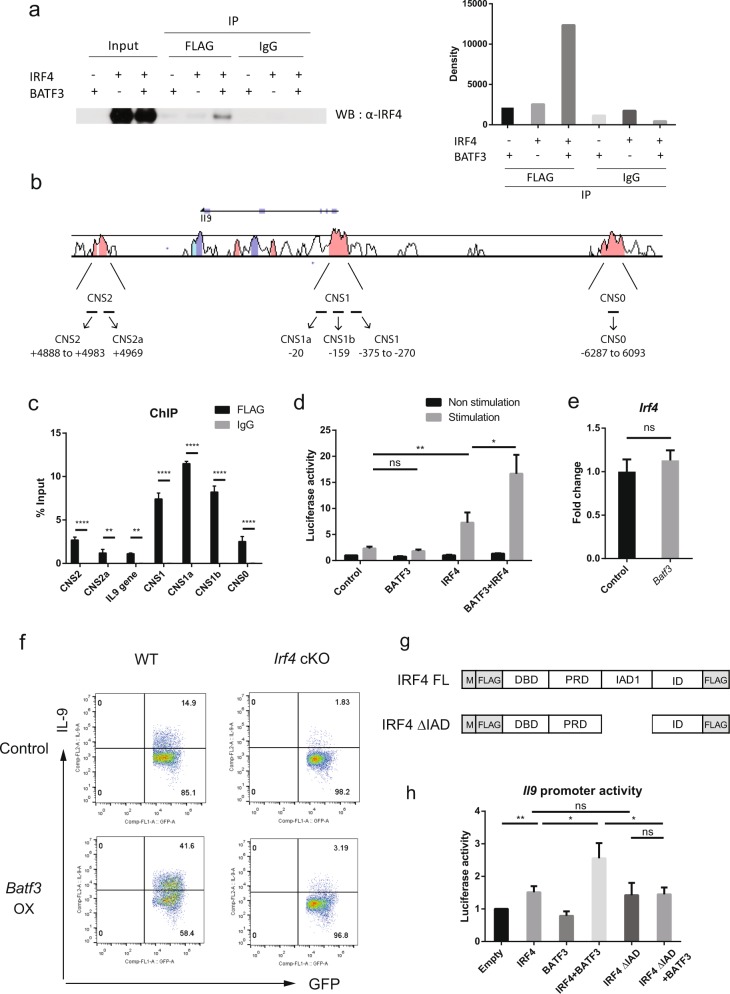
Fig. 3. BATF interacts physically with IRF4 and increases Il9 promoter activity by binding to the CNS1 within the Il9 locus.
a BATF3-FLAG and IRF4 were expressed in HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were precipitated by an anti-FLAG antibody plus agarose or by a control IgG antibody. Precipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting (left), and the immunoblot was quantified by densitometry (right). b The CNSs of the Il9 locus. The numbers indicate the binding sites of the primers. c BATF3-binding sites within the CNSs of Il9 were analyzed in a ChIP assay. Control IgG and anti-FLAG antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation, and qPCR was performed for quantification. d Il9 promoter activity was measured in a transient reporter assay. EL4 cells were transfected with pCMV expression vectors. Cells were stimulated for 4 h with PMA and ionomycin, and were then analyzed in a luminometer. e Expression of Irf4 mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR under control or Batf3-overexpressing conditions. Data were normalized to the levels of Gapdh and are shown relative to controls. f Naive CD4+ T cells from WT and Irf4 cKO mice were transduced with an empty or Batf3 overexpression vector. The cells were stimulated under Th9 conditions for 3 days. Transduced cells were gated for GFP, and then IL-9 production was measured by flow cytometry. OX, overexpression. g Diagram of the IAD domain deletion mutant of IRF4. h Il9 promoter activity was measured by a transient reporter assay. EL4 cells were transfected with CMV vectors expressing the indicated transcription factors and were then stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 4 h. Error bars represent the s.d. P values were calculated using Student’s t-tests. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. All experiments were repeated independently three times.