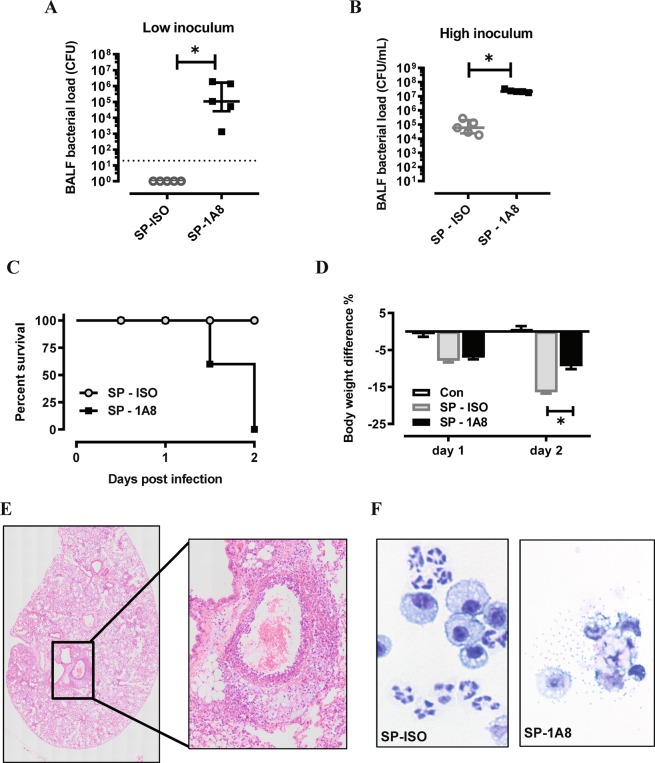
Figure 2.
Neutrophil depletion by 1A8 mAb resulted in uncontrolled bacterial growth in the lungs. (A,B) Lung bacterial load was quantified by serially diluting BALF on horse blood agar supplemented with 5 µg/ml gentamicin. Following overnight incubation at 37 °C, colony forming units (CFUs) were recorded from the highest-countable dilution. (A) Pneumococci in the BAL was cleared by day 2 in the low inoculum model (105 CFU), whereas 1A8 mAb resulted in markedly higher BAL bacterial counts. Dotted line denotes detection limit. (B) In the high inoculum model, SP was detected in the BALF of isotype antibody (ISO) treated mice at day 1 post infection and levels were increased over 2-log in the 1A8 mAb treated mice. n = 5–6, *p < 0.05, two-tailed Students t-tests. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis demonstrated that all mice inoculated with high dose SP and treated with isotype antibody treated (SP-ISO) mice survived, whereas 1A8 mAb antibody treatment (SP-1A8) mice resulted in 100% mortality by day 2. (D) High inoculum SP infection resulted in body weight loss on day 1 and day 2 in ISO treated mice, and the degree of loss was significantly reduced in 1A8 mAb treated mice. n = 5–6, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA. (E) Representative whole slide scan H&E image of lung lobe from SP-1A8 treated mouse on day 2 post high inoculation with insert, identifying significant perivascular and pulmonary oedema with cocci present in this region. (F) Representative image of BAL cells from SP-1A8 mice on day 2 post inoculation identified necrotic macrophages surrounded by pneumococci, which was absent from SP-ISO treated mice.