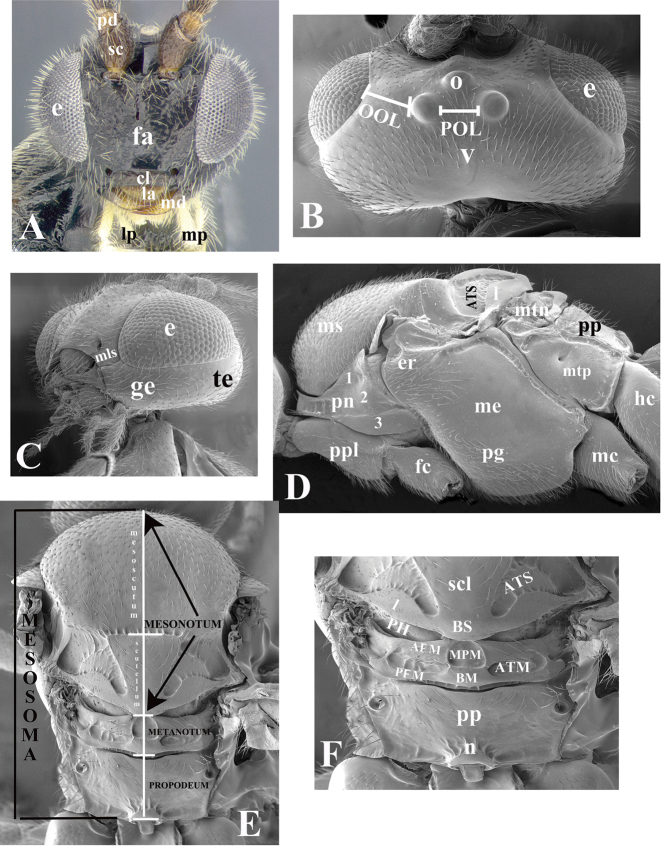
Figure 2.
Head and mesosoma structures Glyptapanteles spp., females A–C Head A Frontal view, G.felipesotoi sp. nov. B Dorsal view, G.alvarowillei sp. nov. C Lateroventral view, G.barneyburksi sp. nov. D, E Mesosoma D Lateral view, G.andybennetti sp. nov. E Dorsal view, G.ianyarrowi sp. nov. F Scutellum, metanotum, propodeum, dorsal view, G.ianyarrowi sp. nov. Abbreviations: cl = clypeus, e = eye, er = epicnemial ridge, fa = face, fc = fore coxa, fr = frons, ge = gena, hc = hind coxa, l = lunule, la = labrum, lp = labial palp, md = mandible, mc = middle coxa, me = mesopleuron, mls = malar suture, mp = maxillary palp, ms = mesoscutum, mtn = metanotum (AFM = anterior furrow of metanotum; ATM = axillary trough of metanotum; BM = medioposterior band of metanotum; MPM = medioanterior pit of metanotum, PFM = Posterior furrow of metanotum), mtp = metapleuron, n = nucha, o = ocellus, OOL = ocular ocelar line (the shortest distance between lateral ocellus and adjacent compound eye margin), POL = posterior ocelar line (the shortest distance between the lateral ocelli), pd = pedicel, pg = precoxal groove, pn = pronotum (1, dorsal rim; 2, central area; 3 ventral rim), pp = propodeum, ppl = propleuron, sc = scape, scl = scutellum (ATS = axillary trough of scutellum; BS = medioposterior band of scutellum, PH = phragma of scutellum), t = temple, v = vertex.