Figure 5. MUC1-C confers NuRD component occupancy on the ESR1 promoter.
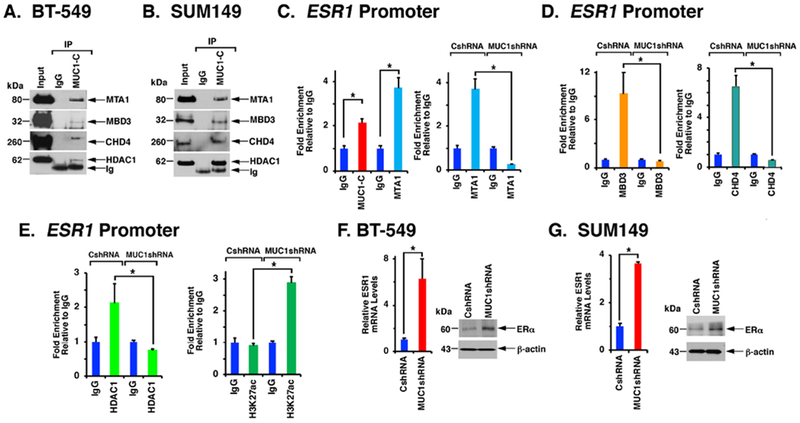
A and B. Nuclear lysates from BT-549 (A) and SUM149 (B) cells were incubated with anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. The precipitates and input were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against the indicated proteins. C. Chromatin from BT-549 cells was precipitated with anti-MUC1-C, anti-MTA1 or a control IgG (left). Chromatin from BT-549/CshRNA and BT-549/MUC1shRNA cells was precipitated with anti-MTA1 or a control IgG (right). D. Chromatin from BT-549/CshRNA and BT-549/MUC1shRNA cells was precipitated with anti-MBD3 (left), anti-CHD4 (right) or a control IgG. E. Chromatin from BT-549/CshRNA and BT-549/MUC1shRNA cells was precipitated with anti-HDAC1 (left), anti-H3K27ac (right) or a control IgG. The DNA samples were amplified by qPCR with primers for the ESR1 promoter (Supplemental Table S2). The results (mean±SD of three determinations) are expressed as the relative fold enrichment compared to that obtained with the IgG control (assigned a value of 1). F and G. BT-549 (F) and SUM149 (G) cells expressing a CshRNA or MUC1shRNA were analyzed for ESR1 mRNA levels (left). The results (mean±SD) are expressed as relative mRNA levels compared to that obtained for CshRNA expressing cells (assigned a value of 1). Lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins (right).
