Figure 5.
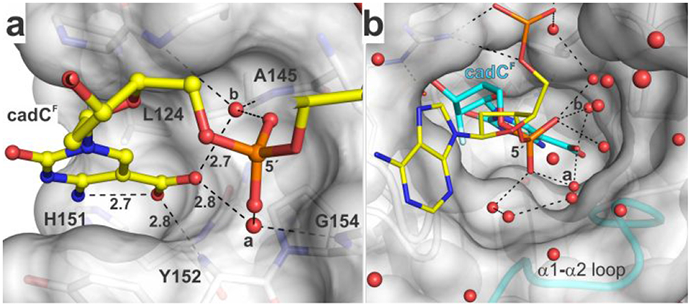
Binding pocket for the caC carboxylate and water molecules that contact this group and populate a channel to the surface. (a) Binding pocket for carboxyl of caC as seen in the structure of TDG82-308 bound to cadCF DNA. Select residues of TDG are shown in surface and stick format, with formatting otherwise similar to that in Figure 4. The 2′-F substituent is not shown (for clarity). (b) Water-filled channel from the TDG active site to its surface. The hydrogen bonding network (dashed lines) could facilitate transfer of a solvent proton to caC. Water molecules that contact the carboxylate of cadC are labeled (a, b).
