Figure 2. Prolonged loss of hepatic Hnf4a with high fat feeding results in the induction of proliferation and inflammation genes in male and female mice.
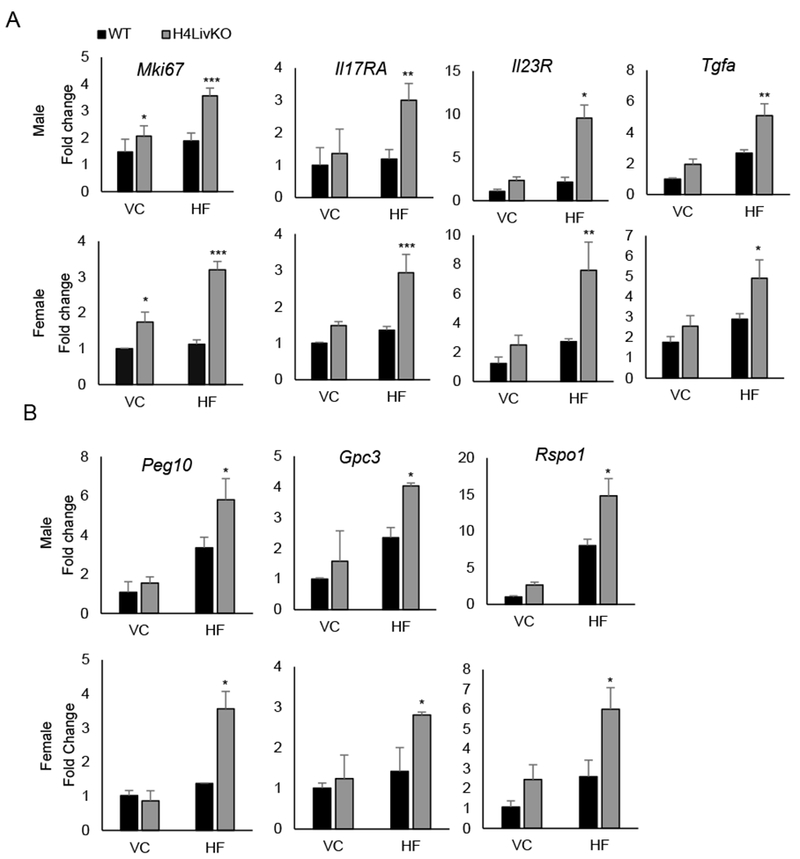
A. Quantitative PCR reveals the hepatic expression of proliferation marker Mki67 and HCC-associated inflammatory markers in WT and H4LivKO mice of both sexes after prolonged feeding on vivarium chow (VC) or high fat (HF) diet. B. Expression of HCC-specific genes in corresponding livers as measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, compared to VC control, *P < 0.03, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005 (N = 4-6) Error bars = SEM.
