Figure 5. Loss of HNF4α combined with high fat diet induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in an IL-6-dependent manner.
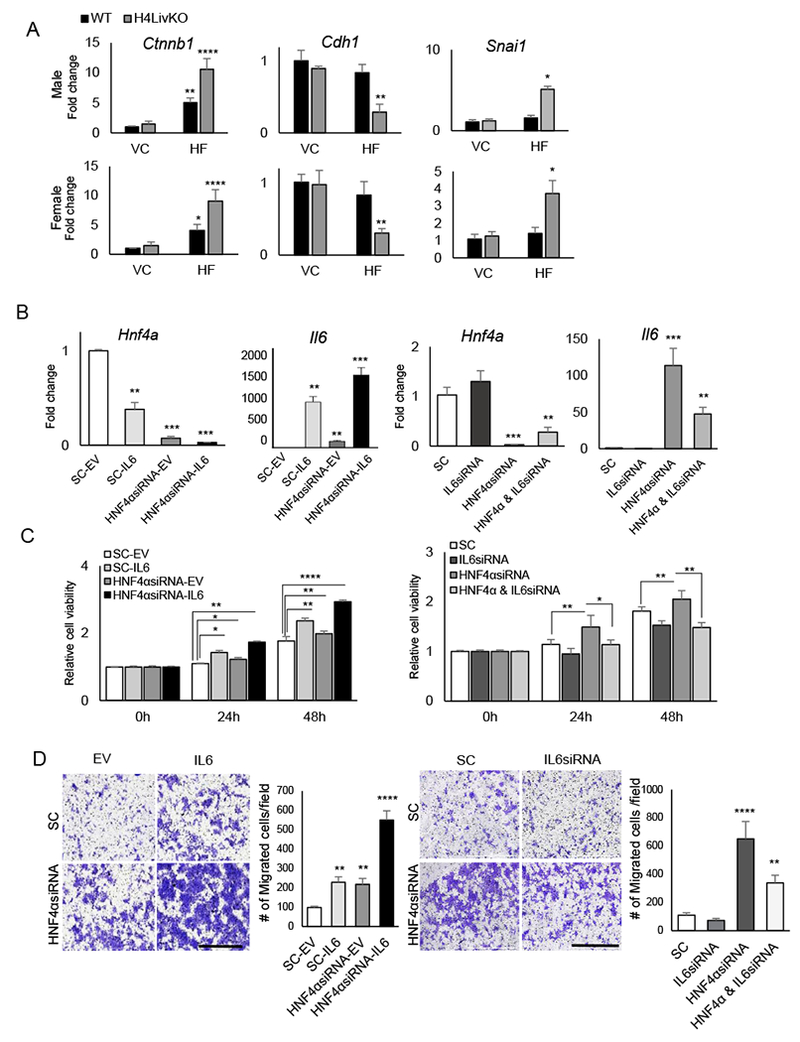
A. RT-PCR reveals mRNA abundance of genes affecting EMT in livers of 38 week-old WT or H4LivKO mice fed vivarium chow (VC) or high fat diet (HF) (N=4-6). B. RT-PCR reveals levels of Hnf4a and Il6 after transfection of AML12 cells with empty vector (SC-EV), scrambled oligonucleotides (SC-IL6), siRNA to Hnf4a (HNF4αsiRNA-EV) or siRNA to Hnf4a with overexpression of Il6 (HNF4αsiRNA-IL6). C. MTT assay reveals proliferating AML12 cells after transfection with empty vector (EV) or Il6 in combination with scrambled or siRNA for Hnf4a (left panel) or with scrambled or siRNA for Hnf4a in combination with scrambled or siRNA for Il6 (right panel) at 24- and 48- h following transfection. D. Migration assay reveals migration of AML12 cells expressing scrambled or siRNA for Hnf4a in combination with empty vector or Il6 transfection (left panel) or with scrambled or siRNA for Hnf4a in combination with scrambled or siRNA for Il6 (right panel), 24-h after plating (N=6). Quantification (right). . Two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, *P < 0.03, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001.
