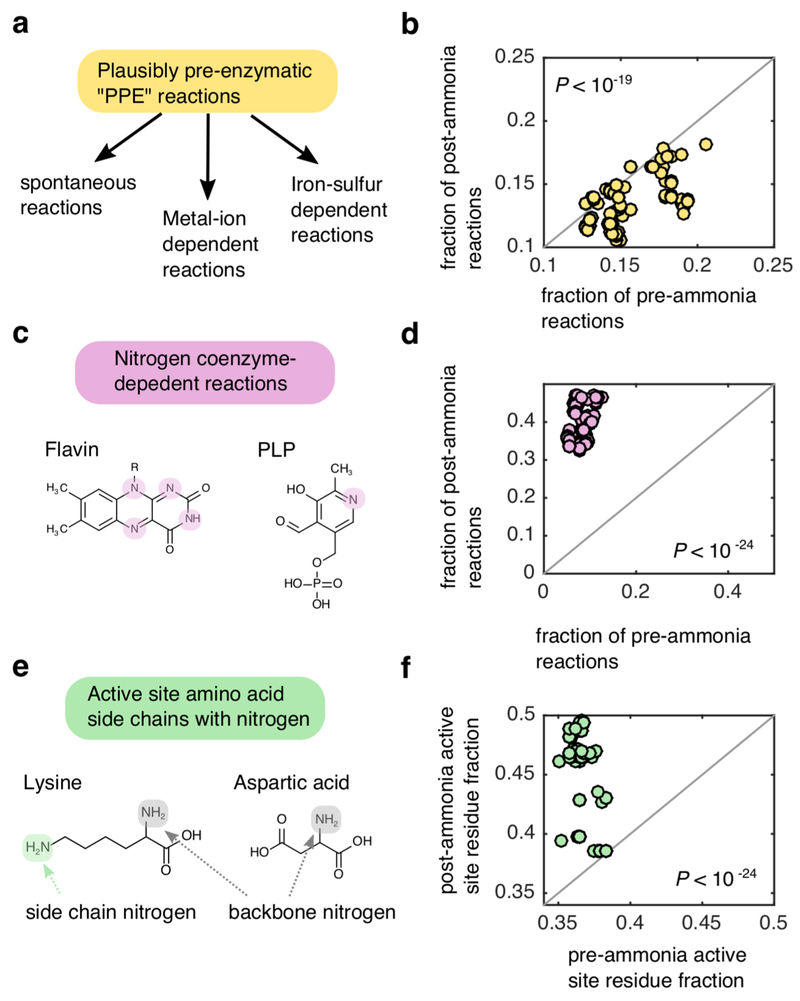
Extended Data Fig 1: Enzymes in thioester-driven protometabolism are depleted in nitrogenous compounds.
(a) We classified reactions in KEGG as being plausibly pre-enzymatic (PPE) reactions if they could (i) proceed spontaneously, (ii) were associated with enzymes that contain at-least one iron-sulfur cluster or (iii) were associated with an enzyme that relied on at-least one metal (Ni, Co, Cu, Mg, Mn, Mo, Zn, Fe, W) cofactor. (b) For all scenarios resulting in expansion of >100 metabolites (n=144) we computed the fraction of PPE-reactions amongst the pre-ammonia reactions (x-axis) and post-ammonia reactions (y-axis). The frequency of PPE-reactions in the pre-ammonia reaction set was on average higher than the frequency of PPE-reactions in the post-ammonia reaction set (one-tailed Wilcoxon sign-rank test: P < 10−19). (c) We identified KEGG reactions that were dependent on at-least one of the following nitrogen-containing coenzymes: flavin, biotin, thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), heme, pterin or cobalamin. (d) We compute the fraction of pre- and post- ammonia reactions associated with nitrogen containing coenzymes in the KEGG database, and found that a much higher proportion of post-ammonia reactions were dependent on these coenzymes relative to pre-ammonia reactions (one-tailed Wilcoxon sign-rank test: P < 10−24). (e) We parsed the catalytic active site database 68 to find entries associated with pre and post-ammonia reactions, and compute the fraction of entries associated with amino acids with nitrogen-containing side chains (Q,N,W,H,K,R). (f) For each scenario, the fraction of active sites with nitrogen-containing amino acids was significantly higher for post-ammonia reactions relative to pre-ammonia reactions one-tailed Wilcoxon sign-rank test: P < 10−24).