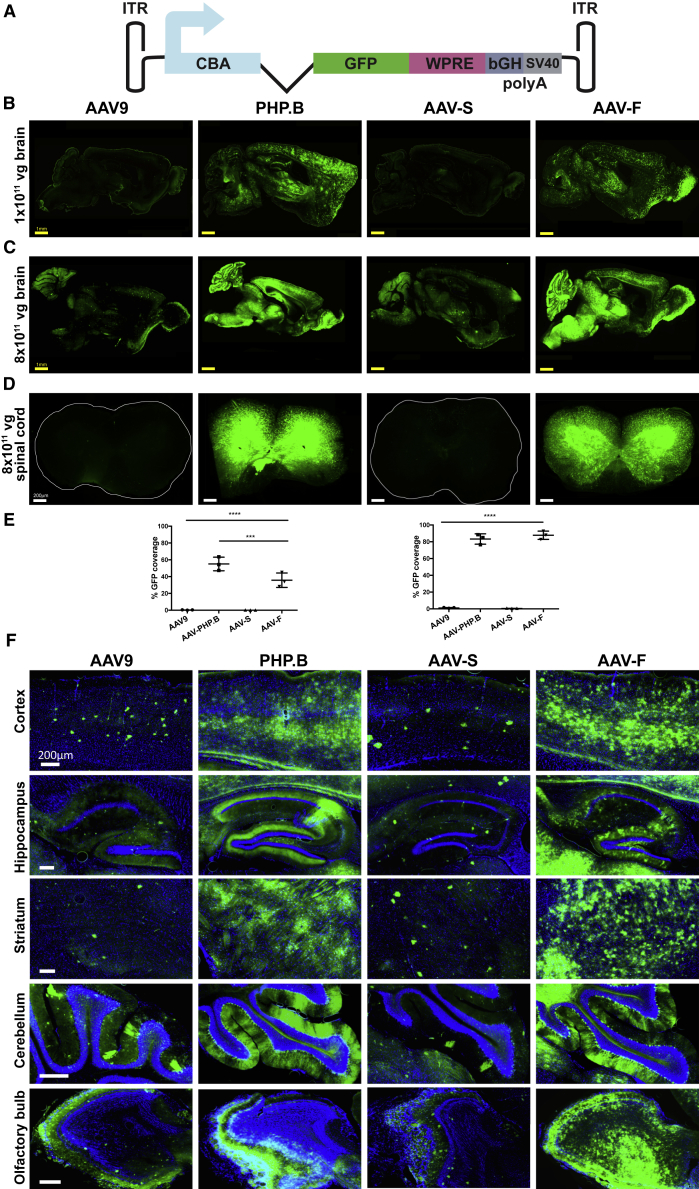
Figure 3.
AAV-F Efficiently Transduces the Brain of Mice after Systemic Injection
(A) Single-stranded AAV-GFP expression cassette used to compare the transduction potential of capsids. ITR, inverted terminal repeat; CBA, hybrid CMV enhancer/chicken β-actin promoter; WPRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element; pA, poly(A) signals (both SV40 and bovine growth hormone derived). (B) Representative low-magnification images of whole-brain sagittal sections from C57BL/6 mice (males) transduced with 1 × 1011 vg (low dose) of AAV9, AAV9-PHP.B, AAV-S, or AAV-F. (C) Representative images of sagittal section of brains after injection of 8 × 1011 vg (high dose) of each vector in C57BL/6 males. (D) Example sections of spinal cords transduced by each of the four vectors administered intravenously at the higher dose (8 × 1011 vg/mouse). (E) Quantitation of native GFP expression from each vector by the percentage of sections covered by fluorescence at low (left panel) and high (right panel) doses. (F) Multiregional comparison of transduction in the brain at the higher dose. ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 after one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (n = 3 mice/group).