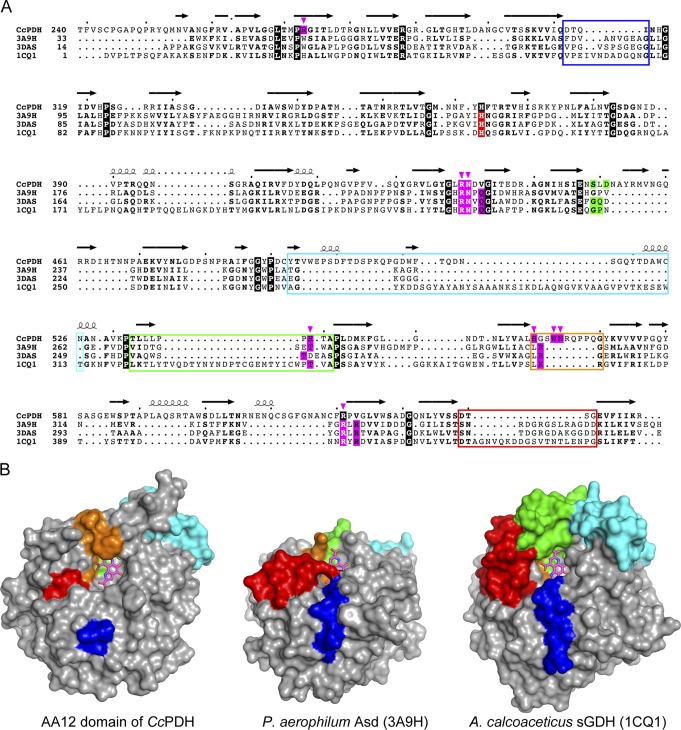
FIG 5.
Comparison of PQQ binding in the AA12 domain and in bacterial PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases. (A) Structural alignment of the CcPDH AA12 domain and bacterial PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases. Perfect matches are enclosed in boxes with a black background. Boxes with magenta and green backgrounds indicate the amino acid residues interacting with PQQ and the active-site calcium ion, respectively, via direct hydrogen bonds. The PQQ-binding residues in CcPDH are indicated by arrowheads and colored magenta. Boxes with a red background indicate the proposed catalytic residues in the bacterial enzymes. Loops forming the PQQ and substrate binding sites are enclosed by colored boxes, as described in the legend to panel B. (B) Comparison of the molecular surface of the AA12 domains of CcPDH (left), Asd (center; PDB accession number 3A9H), and sGDH (right). Loops forming the PQQ and substrate binding sites are colored blue, cyan, green, orange, and red, depending on the position on the β-propeller.