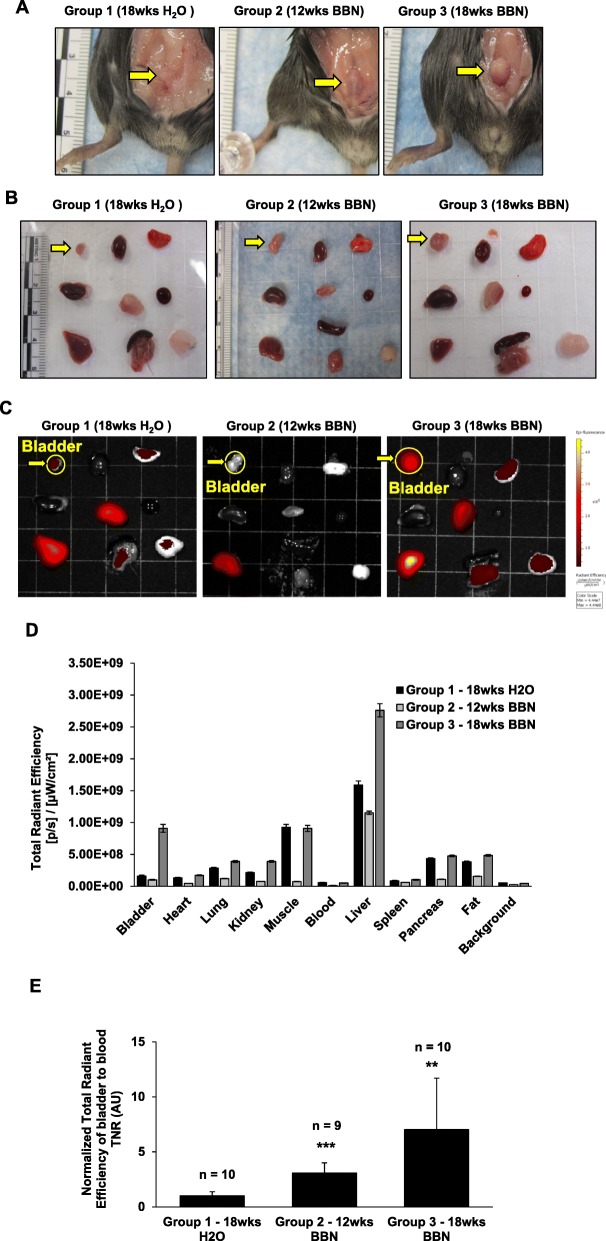
Fig. 2.
Fluorocoxib A uptake by BBN-induced bladder cancer in mice. a After BBN treatment, fluorocoxib A (1 mg/kg, s.c.) was administrated in mice followed by the IVIS imaging. Four hours after fluorocoxib A administration, mice were sacrificed, and dissected tissues were imaged by the IVIS Lumina imaging system. The representative photographs of empty bladders (yellow arrow) from mice from each treatment group. b and c The representative photographs and IVIS ex vivo images of dissected organs of mice. Organs from left to right: Row 1 – bladder (yellow arrow pointed to yellow circle), heart, lung; Row 2 - kidney, muscle, blood; Row 3 - liver, pancreas & spleen, fat. Higher uptake of fluorocoxib A was observed in mice bladder, liver and muscle tissues. d Total radiant efficiency ([p/s]/[μW/cm2]) values of dissected organs from mice from each group (n = 10, n = 9, n = 10). Data show mean ± S.E. of the total radiant efficiency values of individual organs from mice from each group (n = 10, n = 9, n = 10). e Normalized total radiant efficiency values of fluorocoxib A uptake in bladders to blood (TNR). The 3- and 7-fold increase in fluorocoxib A uptake was detected in bladders dissected from mice in Group 2 – 12wks BBN and Group 3 – 18wks BBN (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01), respectively, compared to the dissected bladder from control mice. Data show mean ± S.E. of the normalized total radiant efficiency values of bladder from mice per each group (n = 10, n = 9, n = 10). Significance in fluorocoxib A uptake by bladder of mice from BBN and control groups was assessed using a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)