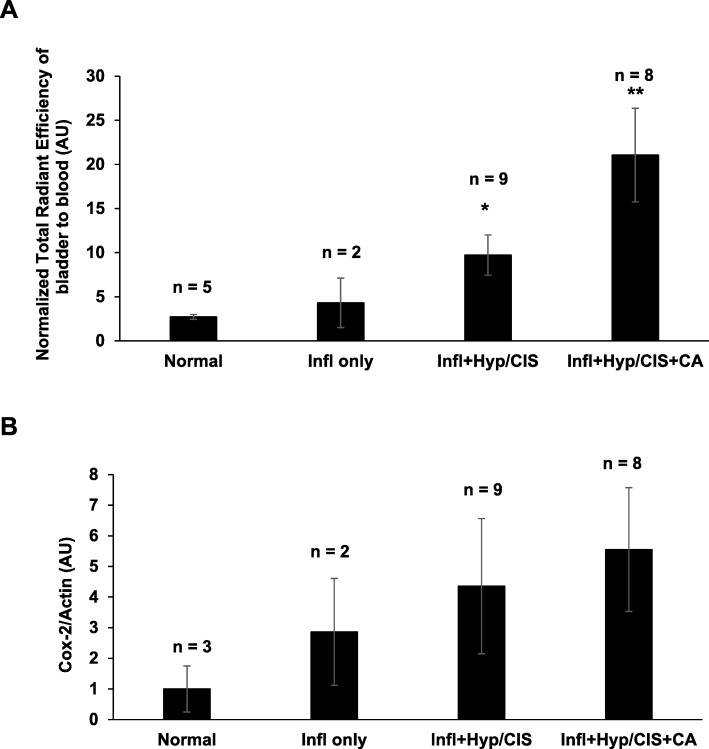
Fig. 5.
Correlation of fluorocoxib A uptake and Cox-2 with the progression of BBN-induced bladder carcinogenesis. a The normalized total radiant efficiency of fluorocoxib A uptake in bladder tissue determined by IVIS imaging system increased with the progression of bladder carcinogenesis determined by histological analysis in a BBN-induced bladder inflammation only (n = 2), bladders with CIS/Hyperplasia and inflammation (n = 9, *p < 0.05) and in bladders carcinoma lesions with CIS/Hyperplasia and inflammation (n = 8, **p < 0.01) as compared to normal bladders (n = 5). b Cox-2 expression determined by WB analysis increased with the progression of bladder carcinogenesis determined by histological analysis (b) in a BBN-induced bladder inflammation only (n = 2), bladders with inflammation and CIS/Hyperplasia (n = 9), and bladder carcinoma lesions with inflammation and CIS/Hyperplasia (n = 8) as compared to normal bladder (n = 3). Data show mean ± S.E. of the normalized total radiant efficiency values or Cox-2/Actin values of bladder from mice per each histologically determined group. Paired Student’s t-test was used to compare the upregulation of fluorocoxib A uptake or Cox-2 expression in BBN-exposed abnormal bladder tissue as compared normal bladders (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01)