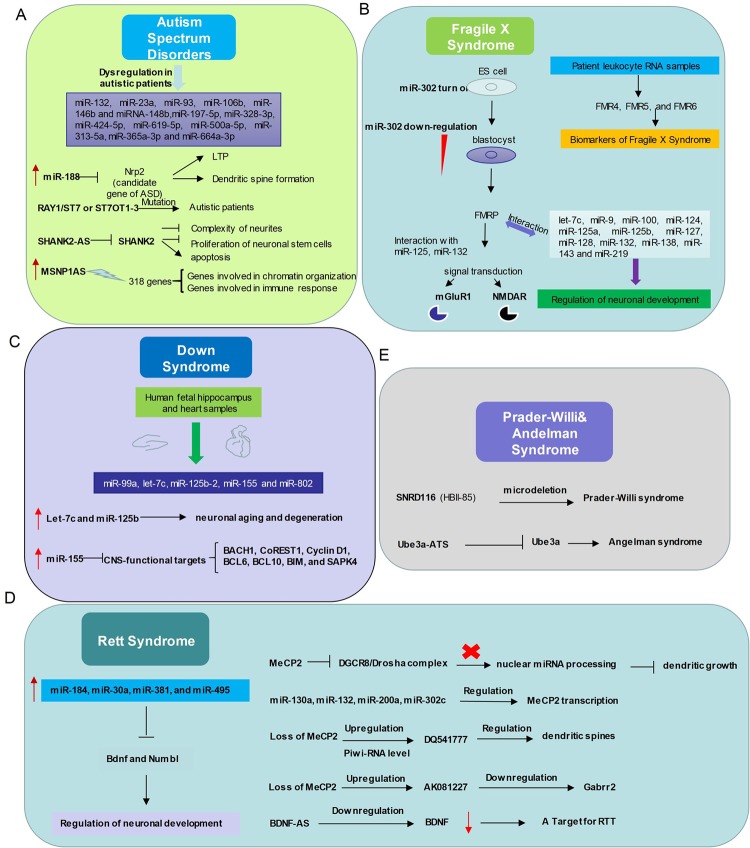
Figure 2.
Relationship between non-coding RNAs and neurodevelopmental disorders. (A) In Autism Spectrum Disorders, miR-132, miR-23a, miR-93, miR-106b, miR-146b and miRNA-148b, miR-197-5p, miR-328-3p, miR-424-5p, miR-619-5p, miR-500a-5p, miR-313-5a, miR-365a-3p and miR-664a-3p expression levels are abnormal. miR-188, RAY1/ST7 or ST7OT1-3, SHANK2-AS, MSNP1AS participate in ASD with distinct ways. (B) The interactions between non-coding RNAs and mechanism diagram of Fragile X Syndrome. microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs regulate Fragile X Syndrome process and might be a class of biomarkers of Fragile X Syndrome. (C) Dysregulation of microRNAs related to Down Syndrome in human fetal hippocampus and heart samples. (D) Left, the expression level of several microRNAs up-regulates in Rett Syndrome patients and these microRNAs play important roles in modulating neuronal development. Right, relationship between Mecp2 and Non-coding RNAs. (E) Microdeletion of SnoRNA SNRD (HBI-85) leads to Prader-Willi syndrome like phenotype. Long non-coding RNA Ube3a-ATS represses Ube3a, which gives rise to Angelman syndrome.