Figure 2.
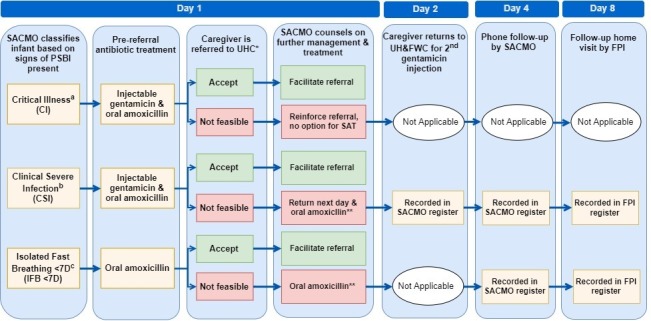
Management and treatment pathway for young infants with PSBI assessed and treated at UH&FWCs according to Bangladesh’s infection management guidelines. *Critical Illness signs: unconscious, convulsions or history of convulsions, unable to feed at all, no movement on stimulation, unable to cry, persistent vomiting, bulging fontanelle, cyanosis. †Clinical severe infection signs: severe chest in-drawing, hypothermia (<35.5°C), fever (>37.5°C), movement only on stimulation, not feeding well (based on history and observation). ‡Isolated fast breathing (<7 days): respiratory rate equal to or greater than 60 breaths per minute as the single sign of infection in infants aged <7 days. §UHC is the primary referral facility; however, the infant may be referred to the district hospital if it is closer to the UH&FWC. ¶The SACMO counsels the caregiver on providing medicine to the infant at home and prescribes oral amoxicillin two times a day for 7 days. FPI, Family Planning Inspector; PSBI, possible serious bacterial infection; SACMO, Sub-Assistant Community Medical Officers; SAT, simplified antibiotic treatment; UHC, Upazila Health Complex; UH&FWC, Union Health & Family Welfare Centres.
