Figure 1.
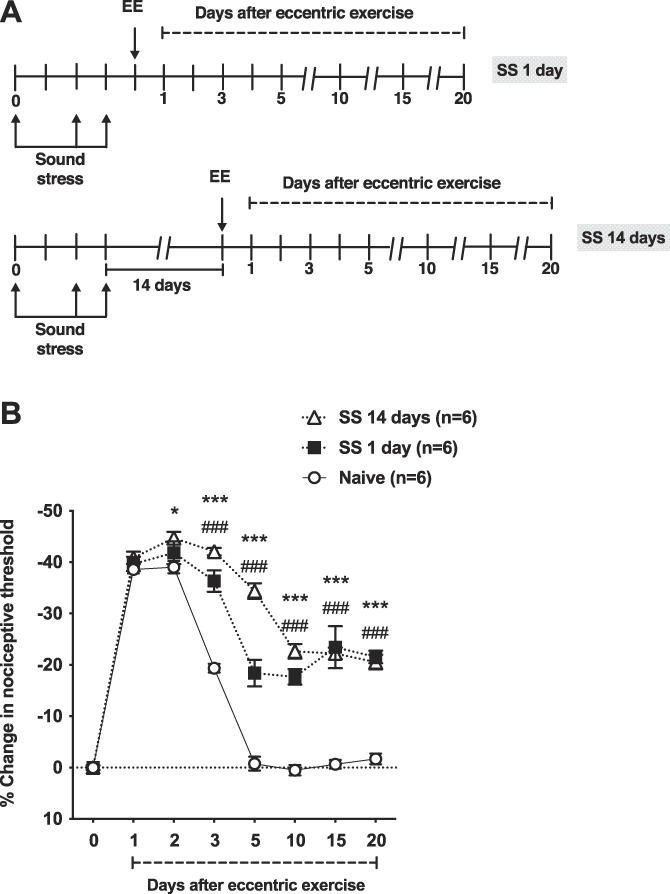
Preexposure to sound stress prolongs eccentric exercise-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. (A) The experimental protocol used to study muscle nociceptive threshold in rats submitted to unpredictable sound stress on days 1, 3, and 4. After assessment of baseline nociceptive threshold sound stress (SS) rats and naive (control) rats were submitted to eccentric exercise 1 (SS 1 day) or 14 (SS 14 days) days after the last sound stress session. The nociceptive threshold was then measured in the ipsilateral gastrocnemius muscle, up to day 20 after eccentric exercise. (B) Two-way ANOVA showed significant effects for treatment (F2,15 = 61.07, P < 0.001), time (F7,105 = 446.9, P < 0.001), and treatment by time interaction (F14,105 = 30.54, P < 0.001). Post hoc analysis revealed significant differences between control rats and SS 1 day rats from day 3 (P < 0.05) to day 20 (P < 0.001) after eccentric exercise. Significant differences between control rats and SS 14 days rats were observed, from day 2 (P < 0.05) to day 20 (P < 0.001) after eccentric exercise. Significant differences between SS 1 day and SS 14 days rats were observed only in days 3 (P < 0.05) and 5 (P < 0.001) after eccentric exercise. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 (Naive vs SS 14 days); ###P < 0.001 (Naive vs SS 1 day). ANOVA, analysis of variance.
