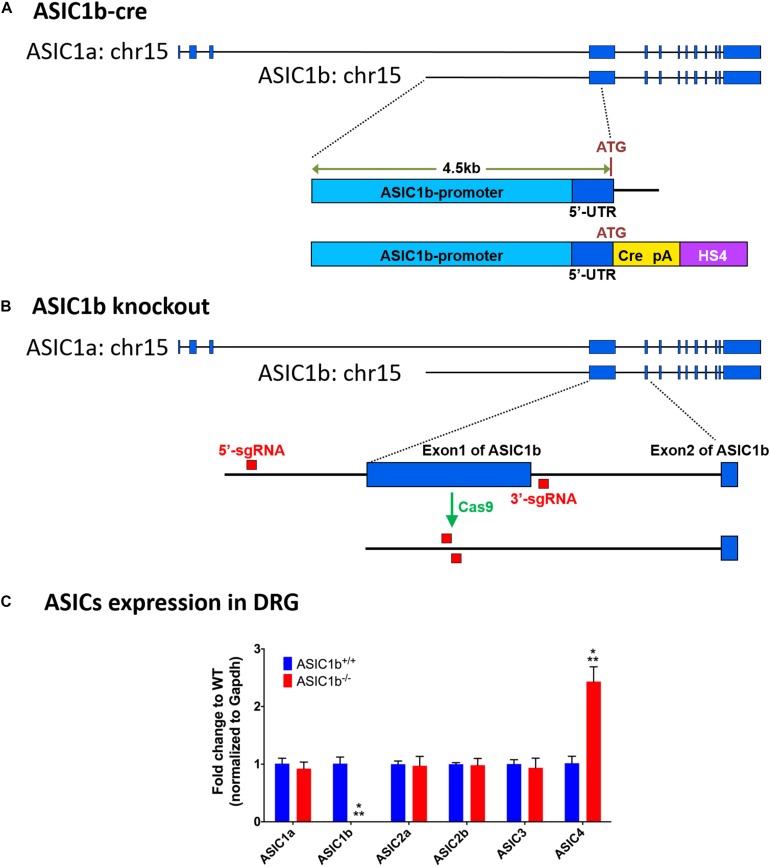
FIGURE 1.
Experimental design of generation of Asic1b-Cre transgenic and Asic1b knockout mice. (A) Generation of Asic1b-Cre mice was based on a 4.5 Kb Asic1b promoter DNA with an insertion of the Cre-polyA-HS4 cassette right after ATG codon. (B) Experimental design of Asic1b knockout via CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Two single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) were used to target the 5′-upstream of exon 1 and the 3′-downstream of exon 1 of Asic1b. (C) The gene expression of ASIC subtypes in the lumbar part of DRG of Asic1b+/+ and Asic1b–/– mice (N = 3). The gene expression levels were analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Compared with the Asic1b+/+, lower expression of Asic1b was detected in the DRG of Asic1b–/– mice. For the expression of Asic1a, Asic2a, Asic2b, Asic3 transcripts, no difference was detected between Asic1b+/+ and Asic1b– /– mice in the DRG. The expression of Asic4 was very low in DRG, although it showed >2-fold difference between Asic1b+/+ and Asic1b– /–. With normalized with gapdh mRNA, the ΔCT mean of ASIC4 of Asic1b+/+ mouse was 10.14 ± 0.32 and of Asic1b– /– was 8.88 ± 0.25, while one of Asic3 of Asic1b+/+ mouse was 4.76 ± 0.19. ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. Asic1b+/+.