Fig. 4.
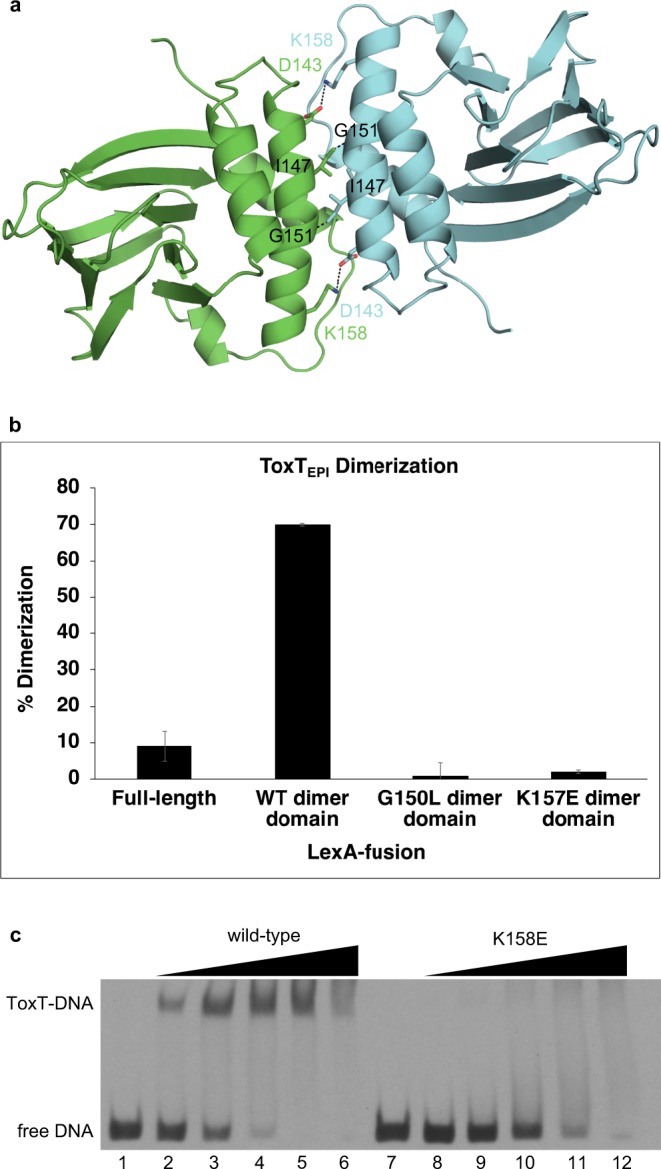
Dimerization of ToxT at the helix α3 interface is required for DNA binding. a Model of the ToxT dimer interface. b LexA-fusion bacterial two-hybrid dimerization assay of ToxTEPI dimer interface mutants. Error bars indicate standard deviation. A western blot of the LexA-ToxTEPI fusions confirming expression is shown in Supplementary Fig. 4. c Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of wild-type and K158E ToxTENV256 binding to the tcpA promoter. All lanes contain 9 nM DIG-labeled 84 bp segment of dsDNA containing the ToxT-binding sites from the tcpA promoter. Lane 1, free DNA; lane 2, 0.098 μg wild-type ToxTENV256; lane 3, 0.195 μM wild-type ToxTENV256; lane 4, 0.39 μM wild-type ToxTENV256; lane 5, 0.78 μM wild-type ToxTENV256; lane 6, 1.56 μM wild-type ToxTENV256; 7, free DNA; lane 8, 0.098 μM K158E ToxTENV256; lane 9, 0.195 μM K158E ToxTENV256; lane 10, 0.39 μM K158E ToxTENV256; lane 11, 0.78 μM K158E ToxTENV256; lane 12, 1.56 μM K158E ToxTENV256. Error bars are indicated (n = 3 experiments). A western blot of the LexAToxTEPI fusions confirming expression of protein has been provided as Supplementary Fig. 4.
