Figure 6.
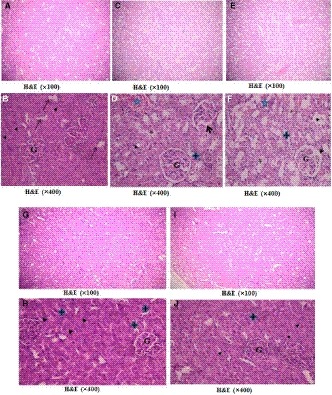
Photomicrographs of H&E‐stained sections of the renal cortex, a and b): the control group showing normal renal architecture formed of renal corpuscles consisting of glomerular capillary tufts (G) surrounded by Bowman's capsule with simple squamous epithelium and narrow Bowman's space. The proximal convoluted tubules (PCT)(▲) were lined with pyramidal epithelium with narrow lumen. The distal convoluted tubules ( )were lined with low cuboidal cells with central rounded nuclei and wide lumen. C&D) The hyperuricemic group showing some shrunken glomeruli (G), widened Bowman's space(arrow), congested blood vessels (
)were lined with low cuboidal cells with central rounded nuclei and wide lumen. C&D) The hyperuricemic group showing some shrunken glomeruli (G), widened Bowman's space(arrow), congested blood vessels ( ), acidophilic vacuolated tubular epithelium (*), pale acidophilic cytoplasm, and pyknotic nuclei. E&F) fructose‐supplemented hyperuricemic group had more shrunken glomeruli (G), widened Bowman's space (arrow), more vacuolated cells (*) in PCT(▲) and in DCT (
), acidophilic vacuolated tubular epithelium (*), pale acidophilic cytoplasm, and pyknotic nuclei. E&F) fructose‐supplemented hyperuricemic group had more shrunken glomeruli (G), widened Bowman's space (arrow), more vacuolated cells (*) in PCT(▲) and in DCT ( ), and acidophilic hyaline casts (
), and acidophilic hyaline casts ( ). G&H) l‐Carnitine‐treated hyperuricemic rats and l‐Carnitine‐treated fructose‐supplemented hyperuricemic rats (I&J) showed apparently normal glomeruli (G), PCT (▲), and DCT (
). G&H) l‐Carnitine‐treated hyperuricemic rats and l‐Carnitine‐treated fructose‐supplemented hyperuricemic rats (I&J) showed apparently normal glomeruli (G), PCT (▲), and DCT ( )
)
