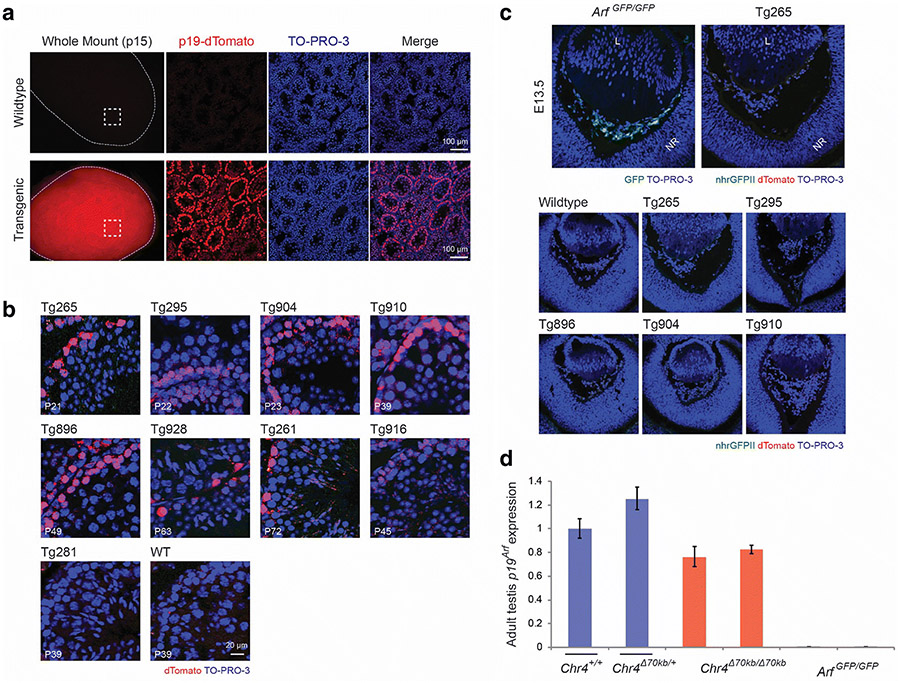
Figure 3.
Detectable expression of the p19-dTomato reporter in the testis but not in newborn mouse eye in BACik-p16G-p19T transgenic animals. a, b Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of and mount (left column) and cryostat sections of the mouse testis taken from wild type and transgenic mice at postnatal day (P) 15 (a) or as indicated (b). The Tg265 transgenic line is displayed in (a); transgenic lines in (b) are indicated. TO-PRO-3 staining highlights nuclei. c Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of cryostat sections show the developing eye in wildtype, Arf GFP/GFP, or BAC transgenic lines (Tg) in mouse embryos at embryonic day (E) 13.5. Note that Gfp expression from the native Arf promoter is readily detected in Arf GFP/GFP animals, but dTomato expression from the p19-dTomato BAC reporter is not. TO-PRO-3 staining highlights nuclei. Definitions – L: lens; NR: neuroretina. d Quantitative analysis of relative Arf mRNA expression, measured by quantitative RT-PCR, using RNA extracted from postnatal testes from wildtype (Chr4 +/+) and transgenic animals as indicated. Arf mRNA expression is normalized to Gapdh and presented as average relative to wildtype animals. Error bars denote standard deviation.