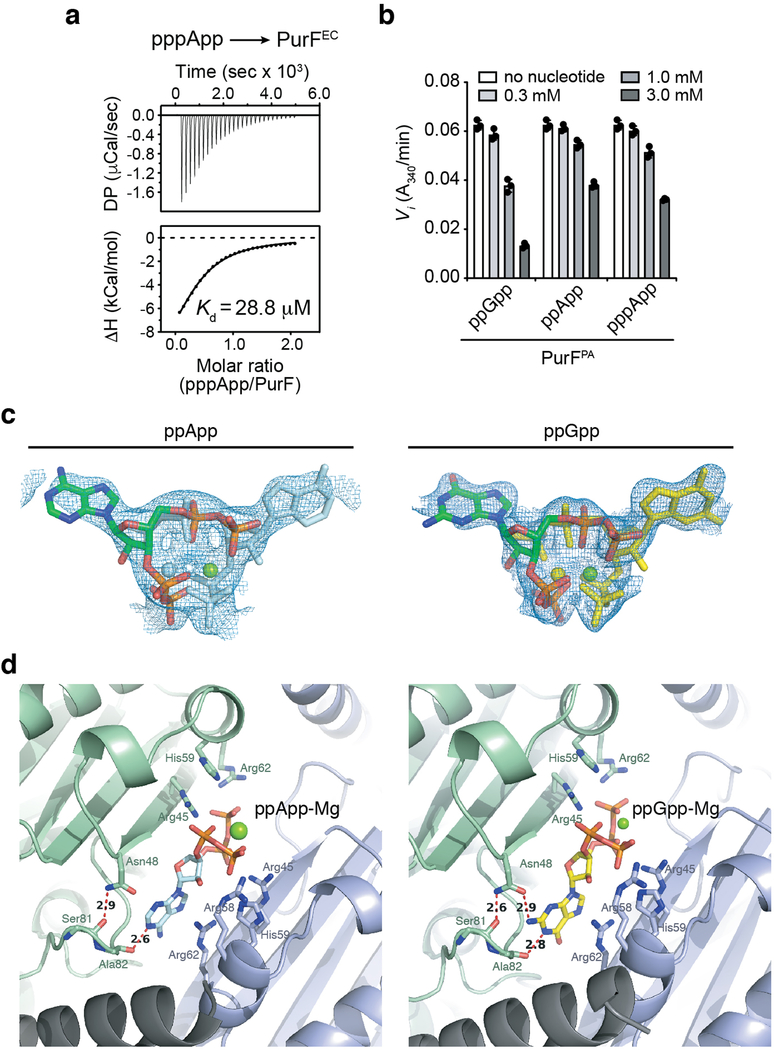
Extended Data Figure 10 |. (p)ppApp binds to and inhibits PurF in a similar manner to ppGpp.
a) Isothermal calorimetry traces (top) and fitted isotherms (bottom) for the titration of 100 μM PurFEC with 1 mM pppApp. Traces are representative of three independent replicates. b) Changes to the activity of PurFPA in the presence of indicated concentrations of ppGpp or (p)ppApp. Data are mean ±SD for three reactions. c) 2Fo-Fc difference electron density maps of ppApp (left) and ppGpp (right, PDB code 6CZF) contoured at 0.4σ are shown in blue. Nucleotides are shown as stick models of two overlapping ppApp-Mg2+ (coloured by heteroatom or light blue) or ppGpp-Mg2+ (coloured by heteroatom or yellow), related by a two-fold rotational axis. d) Comparison of ppGpp and ppApp binding configuration within PurFEC. The nucleotide-Mg2+ complexes are modeled at 0.5 occupancy because they lie on a crystallographic two-fold rotational axis as shown in (c). Relevant hydrogen bonding interactions and their distance in angstroms between PurFEC residues and the purine rings of ppApp (left) or ppGpp (right) are shown with red dashed line.