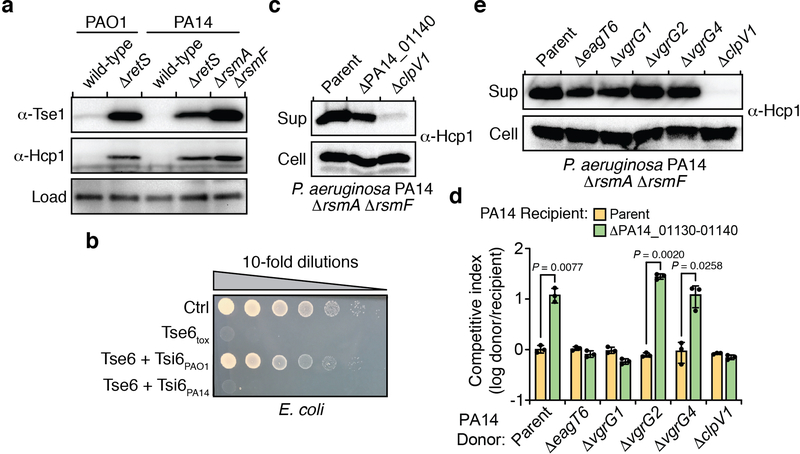
Extended Data Figure 2 |. Characterization of the PA14_01140-PA14_01130-tsi6 gene cluster.
a) Expression levels of the conserved H1-T6SS effector Tse1 and the secreted H1-T6SS subunit Hcp1 are similar between P. aeruginosa PAO1 ΔretS and P. aeruginosa PA14 ΔrsmA ΔrsmF. Western blot analysis of Tse1 and Hcp1 in the indicated P. aeruginosa strains. A non-specific band that reacts with the α-Tse1 antiserum was used as a loading control. b) Tsi6PA14 is not protective against Tse6-mediated intoxication. Viability of E. coli cells grown on solid media harboring inducible plasmids expressing Tse6tox, Tse6tox + Tsi6PAO1, Tse6tox + Tsi6PA14, or an empty vector control. c) Mutational inactivation of PA14_01140 does not abrogate Hcp1 secretion. Western blot analysis of Hcp1 levels in the cell and supernatant (sup) fractions of the indicated P. aeruginosa PA14 strains. d) PA14_01140 delivery into recipient cells requires the H1-T6SS exported protein VgrG1 and the Tse6-specific chaperone EagT6. Intraspecific growth competition assay between indicated PA14 donor and recipient strains. The parental strain genotype is ΔrsmA ΔrsmF. Data are mean ±SD. P values from two-tailed, unpaired t-tests are shown. e) Mutational inactivation of eagT6, vgrG1, vgrG2 and vgrG4 does not abrogate H1-T6SS function. Western blot analysis of Hcp1 levels in the cell and supernatant (sup) fractions of the indicated P. aeruginosa PA14 strains. a-e) Data are representative of three biological replicates.